Join Chris Kuntz for an interview Packaging Insights on how AI and connected worker technology can help the packaging industry overcome the skilled labor crisis.
The packaging industry has been hit by the low availability of skilled workers, but for Chris Kuntz, VP of Strategic Operations at Augmentir, AI systems offer the solution. In this interview with Joshua Poole from Packaging Insights, Chris explores how AI and the Augmented Connected Workforce could revolutionize the packaging industry and how Augmentir’s AI-powered connected worker solution supports optimal efficiencies in manufacturing. He also discusses the importance of effective regulatory frameworks for AI.
This transcript has been edited for clarity and length. View the original video interview on the Packaging Insights website here.
——
Joshua Poole: Hello, everyone. My name is Joshua Poole, and I am the editorial team leader at CNS Media, the publisher of Packaging Insights. I am very pleased to be joined today by Chris Kuntz, who is the Vice President of Strategy at Augmentir, and who is here to talk about the benefits of AI in relation to the packaging industry.
So welcome to you, Chris.
Chris Kuntz: Thank you very much, and thanks for having me, Joshua.
Joshua Poole: So, Chris, AI systems are expected to really transform the wider society but in relation to the packaging industry, to what extent could they revolutionize operations there?
Chris Kuntz: The reality is, to a huge extent. The impact centers around the manufacturing workforce – the people that are part of manufacturing. Historically, the application of AI, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, in manufacturing anyway, has focused on automating repetitive lower-level processes, that replace humans in the factory. Today, what we need to think about, and what we focus on here at Augmentir, is how we can use AI to augment the human workforce. And so, AI, again, used throughout the industry, its served great application from a predictive maintenance, machine failure standpoint, energy efficiency – things like resource utilization and even supply chain visibility and quality control.
And those applications of AI in manufacturing will continue to provide value. But the reality is people are still needed in paper mills, on the factory floor in the areas of safety, quality, and maintenance. There are jobs that just require that humans are there. And that’s not going away any time soon. But what we are faced with, and what many manufacturers are faced with, is these workforce challenges of the aging workforce, the retiring workforce going away. They’re walking out the door with a vast amount of knowledge that is essential to operate factories and plants. Pre-pandemic we had an emerging workforce coming in that maybe didn’t have the necessary skills, but today post-pandemic era, there’s a massive job shortage. There are no workers coming in, and so manufacturers are forced to look at a pool of less-skilled workers to perform tasks that they may not be initially qualified for.
So, it is not just that the skilled labor is going out, it’s just that we don’t have any skills coming in. And so, every manufacturer is faced with a massive labor shortage and as a result a massive shortage of skills required to operate successfully any given day on the shop floor. And that’s really where we think the value is going to come from an AI standpoint, and it’s kind of transformative when you look at historically the application of AI in manufacturing.
Joshua Poole: So, you mentioned the industry is really struggling to overcome the lack of a qualified workforce. How can AI overcome this problem across the industry?
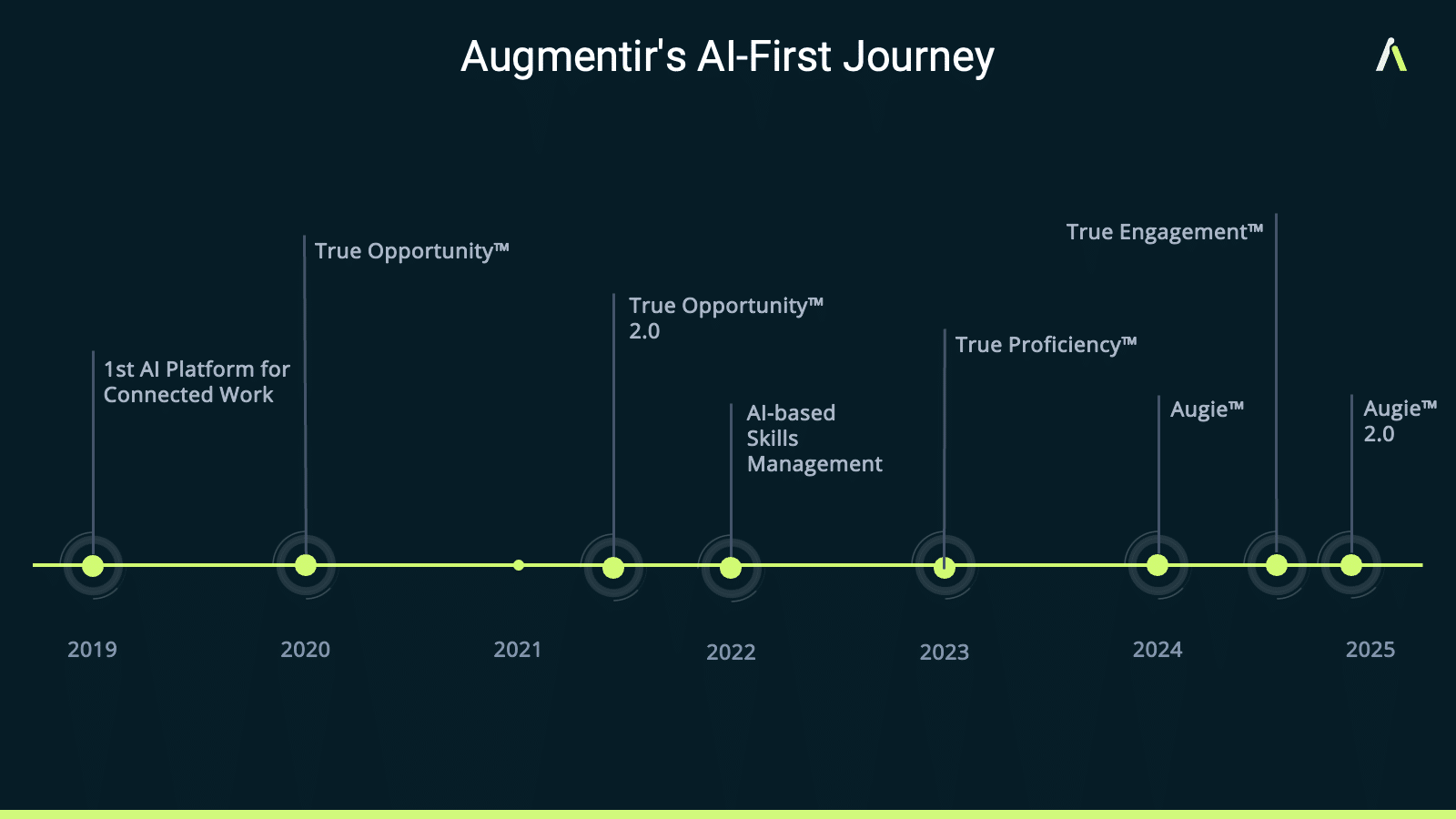
Chris Kuntz: One of the great things about artificial intelligence, and our history as a company, and one of our previous companies was focused on collecting data from connected machines and then using that data and analyzing that data with AI to understand how to make those machines operate better and improve those machines.
From a human standpoint, humans have been relatively disconnected on the shop floor. They’re using paper-based checklists and SOPs and work procedures, the same sort of technology they were using 20, 30 years ago. So, they’re relatively disconnected, and we know little about how they’re operating and how they’re performing and where they need help and where they need assistance.
If we can connect those workers – and I am talking connecting with phones, tablets, wearable devices – if we can connect those workers we have a digital portal into how they’re performing, and through AI we can analyze how they’re performing and then offer them real-time guidance almost like an AI assistant that’s sitting there helping them out if they are struggling, helping them out if they need help, guidance, or support, or if there is a potential safety or security issue that they might be running into.
The same way that AI has historically been used to act on machine data to improve machine efficiency and performance, we can use the same approach for the humans in the factory.
Joshua Poole: Mm-hmm, and can you provide any examples of the ways in which your platform, Augmentir, has benefited companies looking to embrace AI to improve their operations?
Chris Kuntz: Yes, there are a few different ways. More recently we just launched our Generative AI assistant called Augie™. And what that does is that allows workers or operations managers, using natural language, to solve problems faster, assist in troubleshooting, and provide guidance when needed.
One of the first use cases is troubleshooting. This happens every day in a plant, in a paper mill, it happens every day – there’s a problem with a machine, we need to get it back up and running. Otherwise, there’s a downtime issue, which leads to production/revenue loss. And it’s not a standard procedure to fix the machine. And so there’s troubleshooting that needs to happen. This process is very collaborative. But also from a worker standpoint, they typically have to go to 5, 6, 10 different systems to try to find information or talk to different people.
And what a Generative AI assistant can do is be that digital front end to all that wealth of information and return information on, “Hey here’s the solution to this problem. It’s been solved before, it’s in this published guide, here you go.” Or, “You may want refer at this work procedure. This is something, a troubleshooting guide that could help you solve the problem.” Or, “Here’s a subject matter expert that exists” and you can remotely connect to this person who has expertise in this particular type of equipment.
And so being able to give real-time access to that individual at the time of need is critical. And I think the other big area, at least early on here, is around training.
So, if you think about the skilled labor, workforce shortage, the tenure rates in manufacturing, people are quitting faster. They’re not sticking around for 15 years, they’re sticking around for three years, maybe, possibly, at max. And so, training and learning and development, HR leaders have to think about how to change onboarding practices because it’s not practical anymore to onboard someone for six months if they’re only gonna be around for nine months.
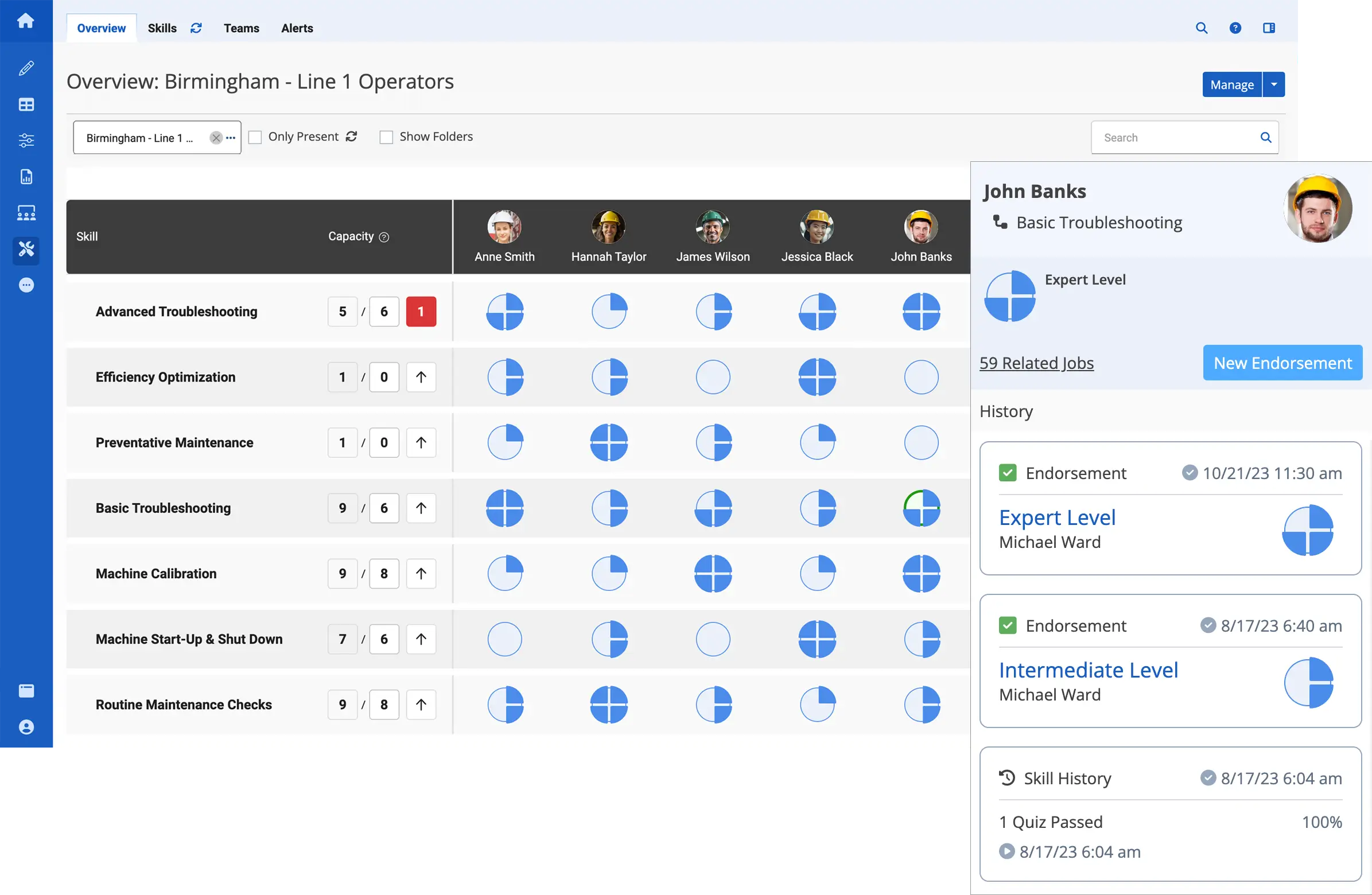
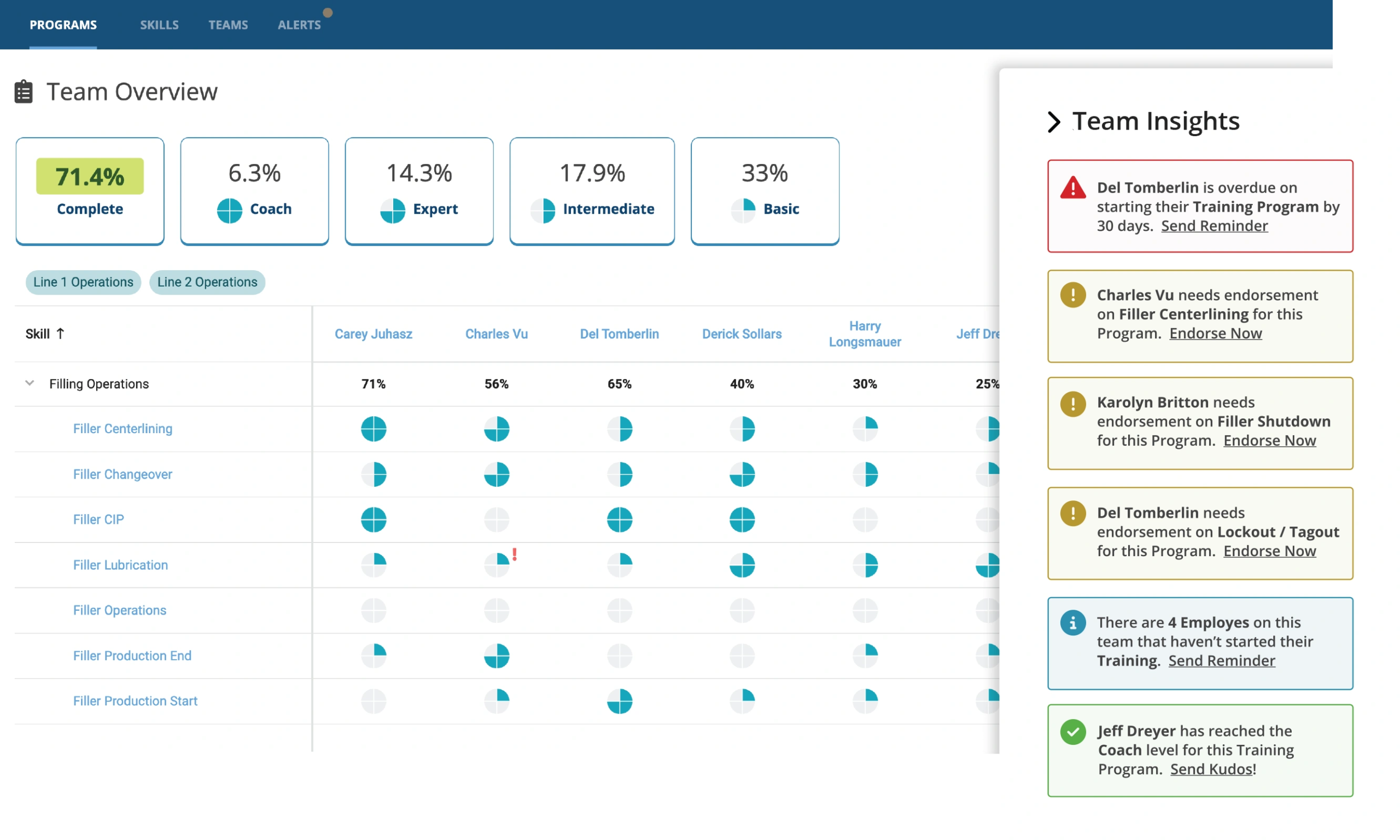
And so the goal, with many of the organizations that we speak with, the goal is to reimagine and rethink training and move it away from the before they’re productive in the classroom to move it onto the floor. Move it into the flow of work, they call it. And so what we can do with AI there is, we don’t understand that worker or their skill level or their competency levels. And if that’s digitally tracked, we can use AI to augment those work instructions and work procedures to say, “Hey, you’re a novice. This is your first month on the job. You’re required to watch this safety video before you do this routine.” And if you’re an expert worker, maybe you wouldn’t be required to do that. Or if you were trained, but your performance is lagging vs. the benchmark, we can come – the instructions can come and be dynamically adjusted to say, “Hey, here’s some additional guidance to help you through this procedure and through this routine.”
So, it gives visibility and insight into areas. I mean, if you had three people on the shop floor, you’d probably know exactly what they were doing. But once you get some larger organizations and they have dozens of people or hundreds of people, it becomes much much harder to understand where the opportunities for improvement are. And AI has the ability to do that, certainly in the training area.
Joshua Poole: Hmm, that’s very interesting. And of course, AI is largely unregulated worldwide, which can create problems like AI washing and irresponsible use. But what do you see as the biggest concern with the proliferation of AI systems within the packaging industry?
Chris Kuntz: So, certainly there’s a lot of concerns with respect to that, and for Augmentir, our approach is we leverage a – certainly from a Generative AI standpoint, we leverage a proprietary, fit-for-purpose, pre-trained large language model that sits behind our Generative AI solution. And when you combine that with robust security and permissions that can help factory managers, operators, and ever engineers or frontline workers only have access to the information that they need, and still provide the benefits of problem-solving faster and improved collaboration.
One of the other things though that I think is really important is this concept of “verified content” – so we’ve all used ChatGPT, right? And early on, I think they had this disclaimer, ChatGPT is 90% correct, so it could return false data. That’s not just not acceptable in an industrial settting. You can’t say, “Here’s a routine to do a centerlining on a piece of equipment” and have someone stick their hand in a place and get it chopped off. You can’t be 90%, you have to be 100%.
So, we have a concept of our Generative AI system, the ability to return verified and unverified data, and then the organization can decide what they want to do with that. So, if it’s a frontline worker, maybe, if it is unverified data, it’s labeled, and you need a supervisor that has to come over if you are going to perform that routine. And then the ability to sort of take the information that comes back and categorize it in terms of verified data, unverified data, and then be able to control how you’re using that. So, it’s not the wild wild west, it’s a very controlled environment. The scope of, if you think about our, in our world, if we’re serving a manufacturing company – and Augmentir is being used for digital manufacturing in paper and packaging companies like Graphic Packaging and WestRock, and so the information that, in our scope of their world is corporate documentation, engineering documentation, operational data, work order data, people data – could be their skills matrix and training history and things like that, but it’s all contained within their enterprise. We’re not looking outside of that, it’s really a constrained data set. And that’s what feeds our large language model.
That significantly helps the application of this, there are people that are exploring using more open AI and GPT models to do this. But then you run into the problems that you said, where there’s a lot of information that both you are feeding into the AI, which could be a security risk, and then the information that you are getting back that could be a security risk.
Joshua Poole: Okay, and as a final question. What advice would you give to politicians working to establish these regulatory frameworks for AI systems?
Chris Kuntz: Great question.
You know, our point of view is we think, you know President Biden had the AI regulation executive order here in the United States back in October, we think it’s much needed on several fronts. Certainly, every company now is saying that they’re an AI company and trying to sprinkle in AI to everything they do. And some of that can be a little problematic.
But at least in the U.S. here in Biden’s AI regulation executive order, there was a lot of talk about job disruptions and putting focus on the labor and union concerns related to AI policies. I think that reinforces our use of AI as a way to augment workers. We’re not looking to replace workers and it’s addressing a huge problem. I think the Department of Labor, they’re issuing guidance to employers around AI that you can’t use it to track workers and you can’t use it to, you know there’s labor rights that exist in the world. And I think that gets back to having these AI co-pilots or Generative AI assistants that can help workers perform their jobs safely and correctly, maximizing the potential. It’s really where on-the-job learning comes into play. It’s things that were happening off the factory floor before. Now it’s squarely suited to help address some of the big manufacturing labor workforce problems that exist today. So, there’s a lot of language in that executive order around making sure that AI is used, not just responsibly, but used for purposes that are going to further the industry. And again, that’s squarely where we sit in terms of workforce development and using it to address the labor shortages from a training and support standpoint.
But, overall, I think, absolutely we embrace the regulatory – Generative AI regulation – and control aspects of this because it could become problematic if you are not doing that, for sure.
Joshua Poole: Mm-Hmm that’s very interesting. Chris, thanks for your time today.
Chris Kuntz: Yes, thank you very much. Thanks for having me.