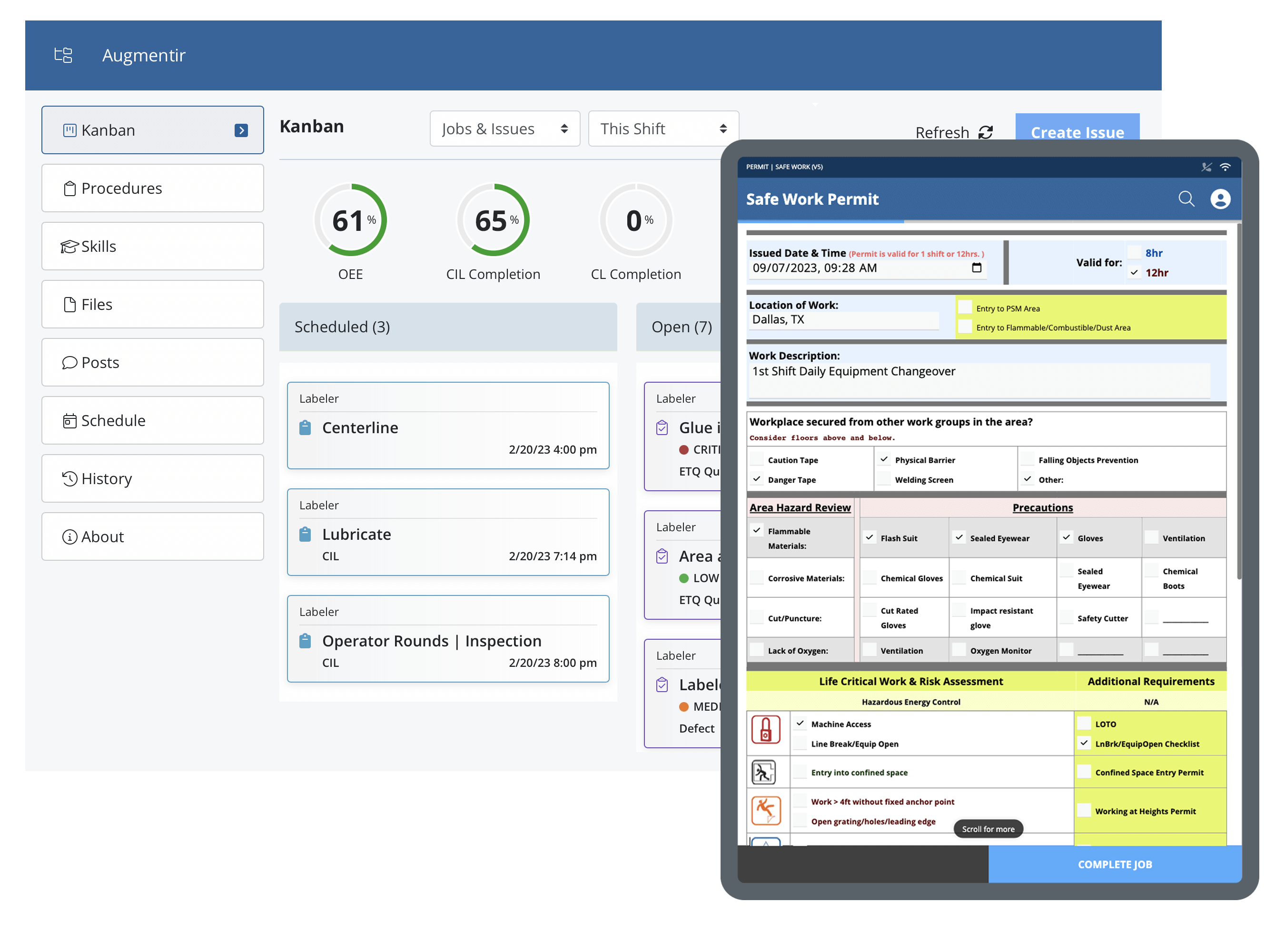
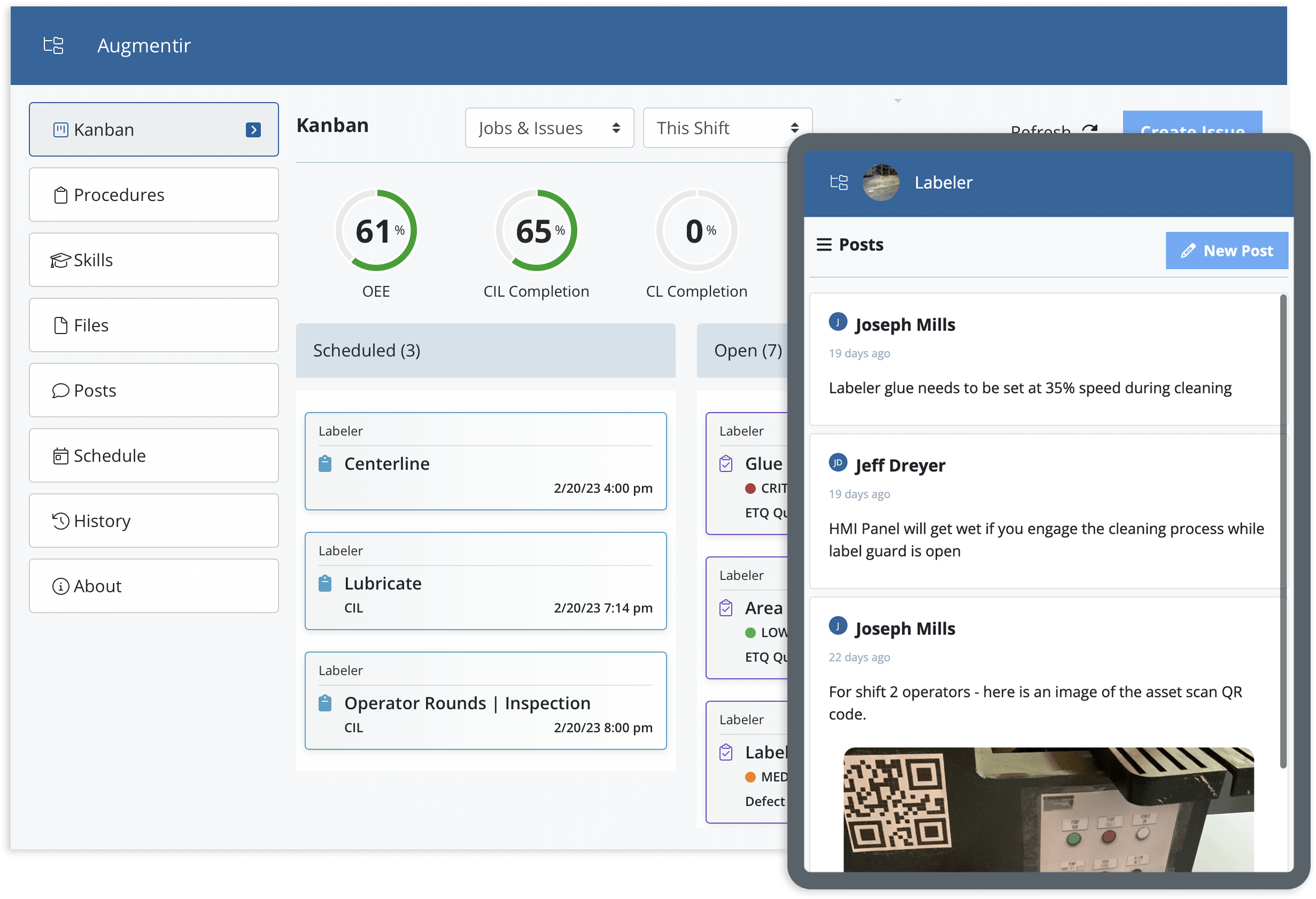
In manufacturing and industrial operations, many common tasks involve potential hazards that could result in accidents, injuries, or damage if not properly controlled. According to the National Safety Council, 33% of workers reported being exposed to permit-to-work failures and 14% of workers said that PTW failure had caused or contributed to a serious injury in their workplace.
Tasks that often require PTW processes have a high-risk factor, examples of manufacturing work that fall under this category are:
Lockout Tagout (LOTO): Permit-to-work processes and systems are critical to the success and safety of all lockout tagout-associated tasks. These activities can be complex and dangerous, requiring certifications and practical experience to keep workers and operations safe. A proper PTW system helps reduce the risk of accidents and minimize worker injuries.
Working at Heights: Tasks performed at elevated levels, such as on scaffolds, platforms, or rooftops, can lead to falls and serious injuries. A PTW ensures that appropriate fall protection measures are in place.
Confined Space Entry: Entering confined spaces like tanks, vessels, or tight spaces can pose risks such as oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, or physical entrapment. A PTW ensures that workers follow strict safety protocols during entry and exit.
Equipment Maintenance and Repair: Maintenance and repair work on machinery and equipment can expose workers to moving parts, electrical hazards, and other risks. A PTW helps ensure that proper lockout-tagout procedures and safety precautions are followed.
While specific tasks requiring a permit-to-work system vary based on the industry, an organization’s specific safety policy, and a variety of other factors, implementing a properly structured PTW system can minimize risks, enhance frontline worker safety, and ensure compliance with safety regulations and standards.