Discover key strategies to boost production efficiency in manufacturing—maximize output, cut waste, and improve operations with smart, practical solutions.
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, production efficiency in manufacturing is a critical factor that directly impacts profitability, customer satisfaction, and long-term business success. To achieve production efficiency, the actual output must match the optimal standard output, which involves minimizing waste, reducing downtime, optimizing labor, and ensuring consistent quality at every step of the manufacturing process.
Introduction to Production Efficiency
Production efficiency refers to the ability of a manufacturing process to produce the maximum output with the given resources, while minimizing waste and reducing costs. It is a key concept in economics and operational analysis, essential for businesses to remain competitive in the market. Achieving production efficiency involves optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving productivity to achieve higher profitability and competitiveness. By focusing on improving production efficiency, manufacturers can increase their production capacity, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. This, in turn, leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, as high-quality products are delivered consistently and on time.
What is Production Efficiency in Manufacturing?
Production efficiency refers to the ability of a manufacturing operation to produce goods using the least amount of resources—time, materials, and labor—without compromising on quality. An efficient production line runs smoothly, minimizes bottlenecks, and ensures equipment and workforce are fully utilized. To measure production efficiency, metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), cycle time, yield rates, and labor productivity are used.
Using digital tools, AI-powered analytics, and connected worker platforms are revolutionizing how factories operate. These technologies provide visibility into operations, uncover hidden inefficiencies, and support agile decision-making.
Why is Production Efficiency Important?
In manufacturing, even small inefficiencies can lead to significant cost overruns, missed deadlines, and quality issues. Improving production efficiency is essential for maximizing output while minimizing input—helping manufacturers stay competitive, agile, and profitable in an ever-evolving market. Manufacturing efficiency, on the other hand, focuses specifically on optimizing the effectiveness of manufacturing processes, workforce deployment, and overall productivity on the shop floor. Efficient production processes enable manufacturers to do more with less, which not only boosts the bottom line but also enhances the overall customer experience.
Here are some of the key benefits:
Lower Operational Costs
By reducing machine downtime, optimizing labor, and minimizing material waste, companies can optimize processes to significantly cut overhead costs and improve profitability.
Reduced Waste and Rework
Quality control ensures that products are made right the first time, decreasing scrap rates and minimizing costly rework caused by defects or human error.
Shorter Lead Times
Streamlined workflows and fewer production delays, coordinated through efficient production schedules, mean faster turnaround times, allowing manufacturers to fulfill orders more quickly and meet tight delivery schedules.
Better Resource Utilization
Whether it’s labor, machinery, or raw materials, efficient production ensures every resource is used to its full potential throughout the entire production cycle—maximizing value and reducing idle time.
Higher Customer Satisfaction
Consistently delivering high-quality products on time builds trust with customers and strengthens relationships, leading to repeat business and positive brand reputation. Manufacturers improve efficiency by leveraging modern technologies and real-time data analytics, which helps streamline processes, reduce downtime, and enhance productivity.
Greater Competitiveness in the Market
Manufacturers that improve efficiency can offer better prices, respond faster to market changes, and innovate more effectively—gaining a clear edge over less agile competitors.
Ultimately, production efficiency is not just about internal gains—it’s a strategic advantage that drives growth, scalability, and long-term success.
Key Strategies to Improve Production Efficiency
Here are some proven strategies to improve production efficiency:
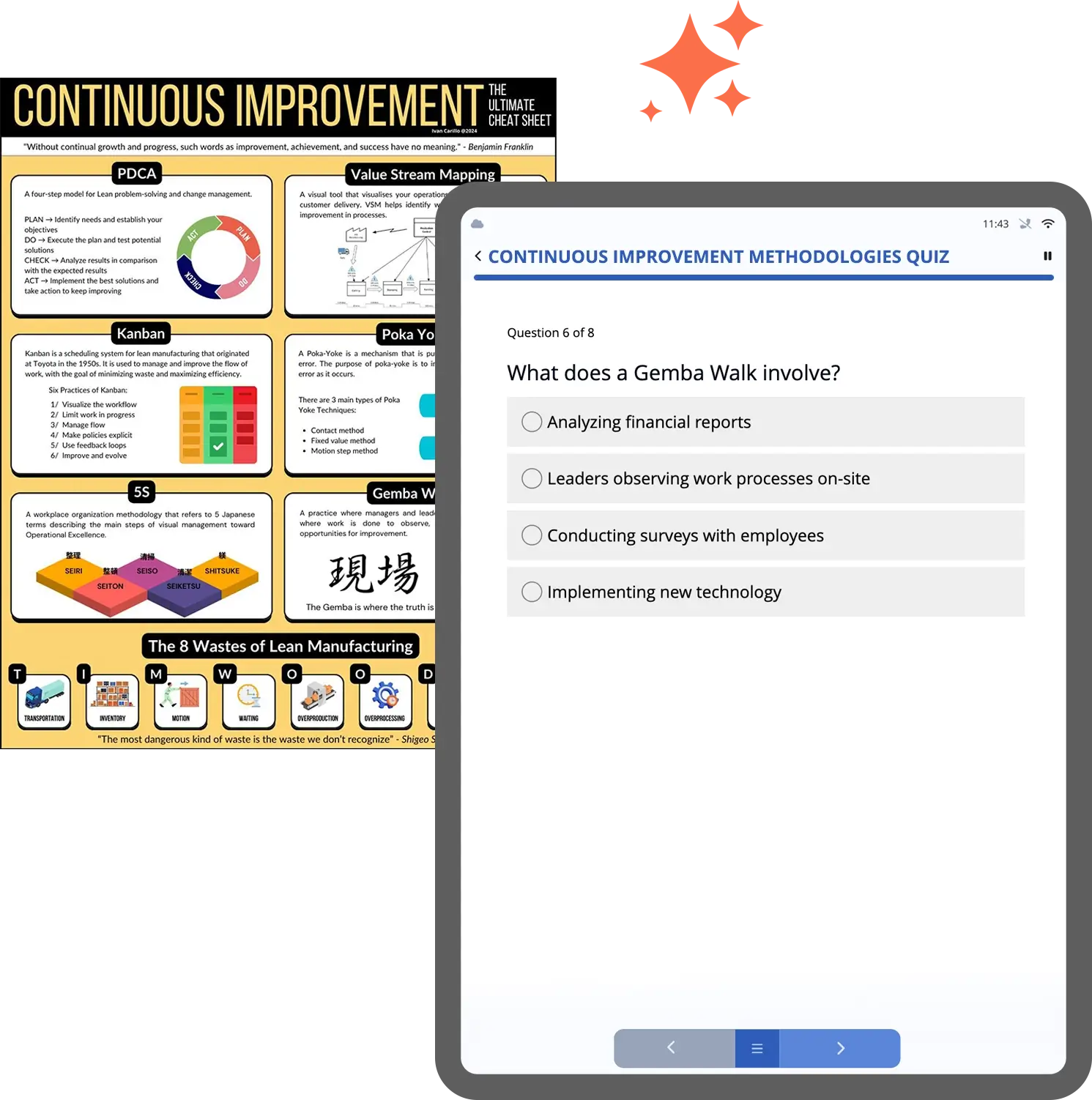
1. Implement Lean Manufacturing Principles to Drive Continuous Improvement
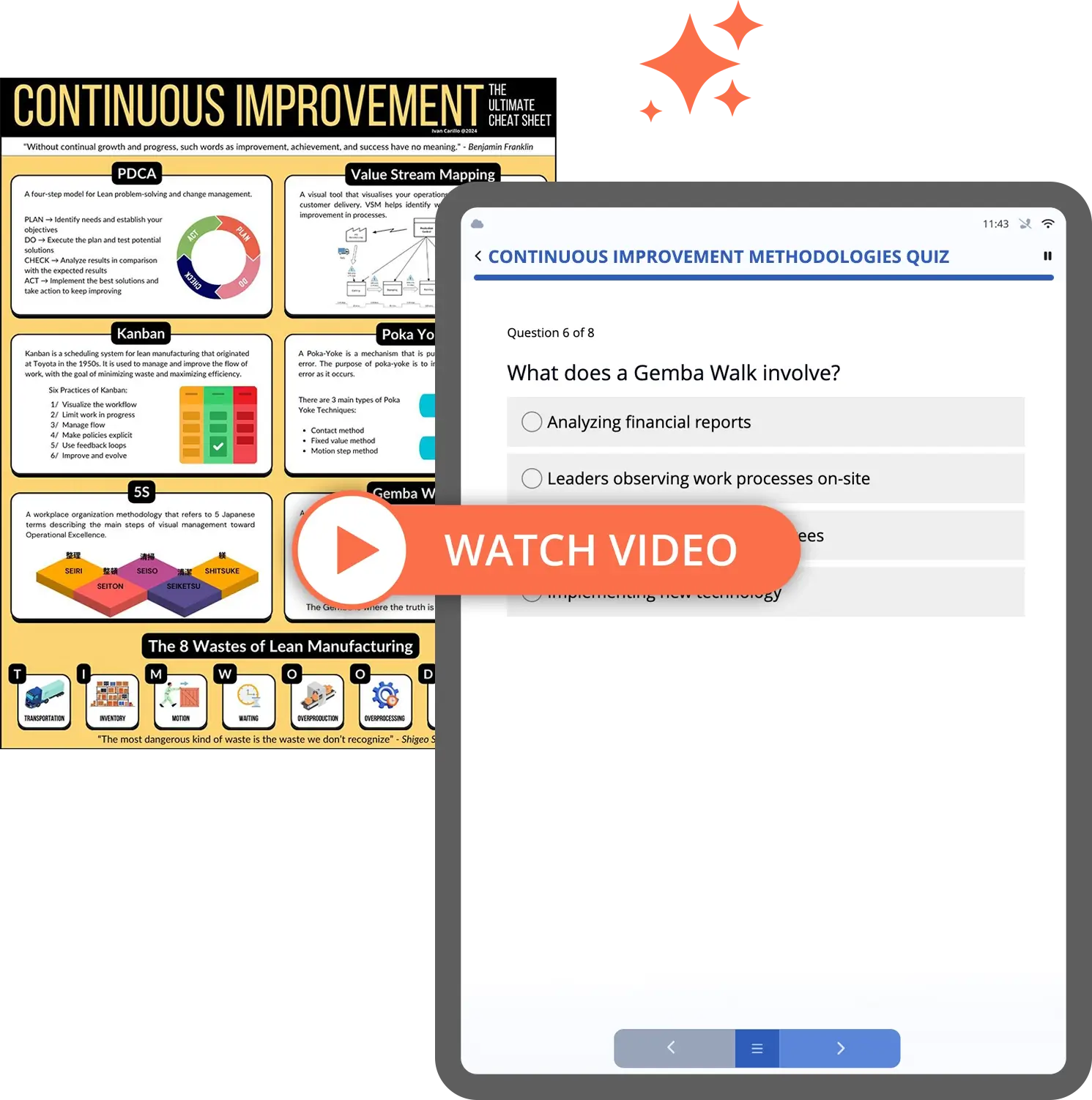
Lean manufacturing methodologies focus on improving efficiency by eliminating waste (or “muda”) from every aspect of the production process. Tools such as 5S Audits, Kaizen, and value stream mapping help identify inefficiencies and areas for continuous improvement.
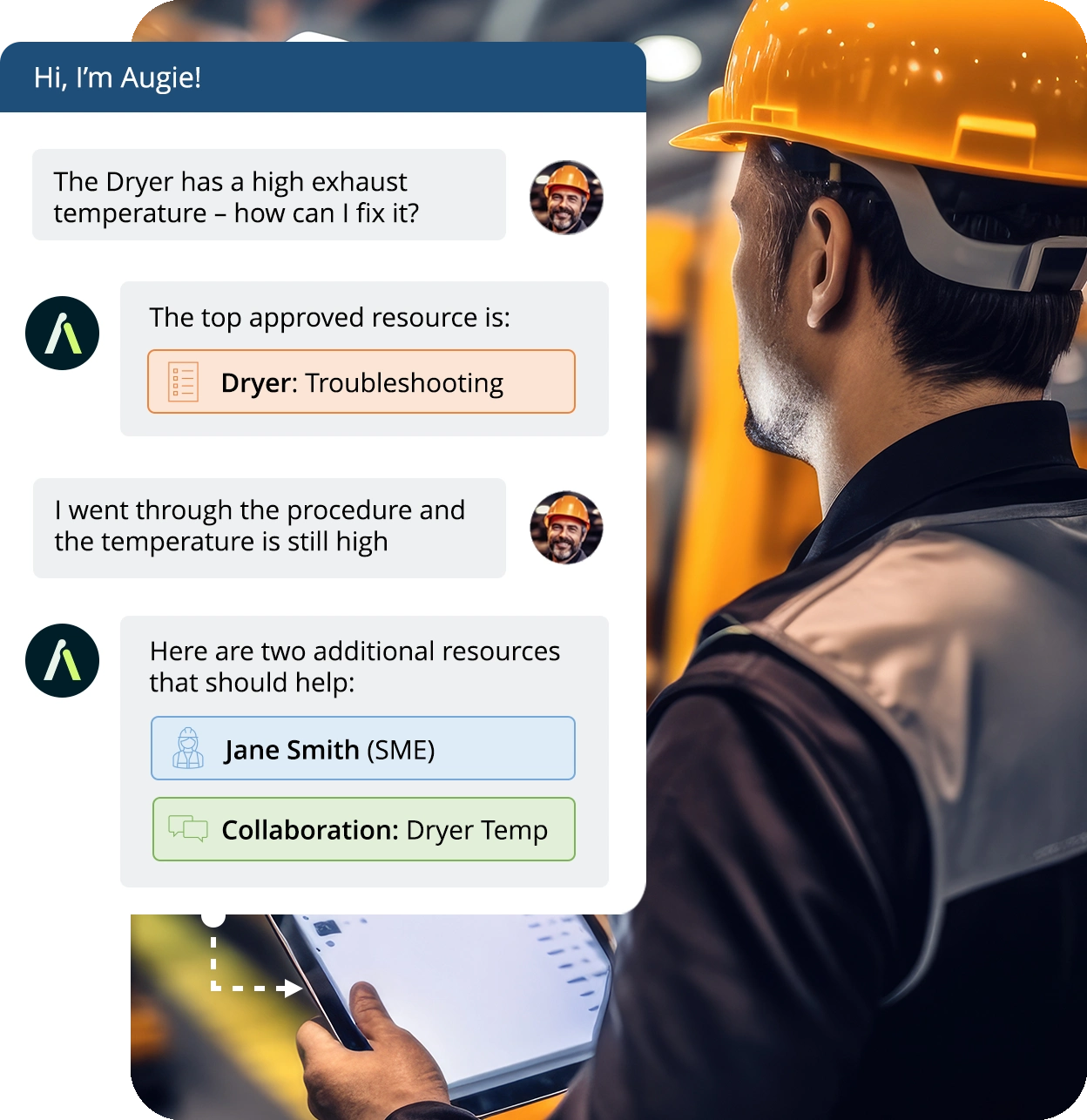
2. Invest in Autonomous Maintenance and TPM
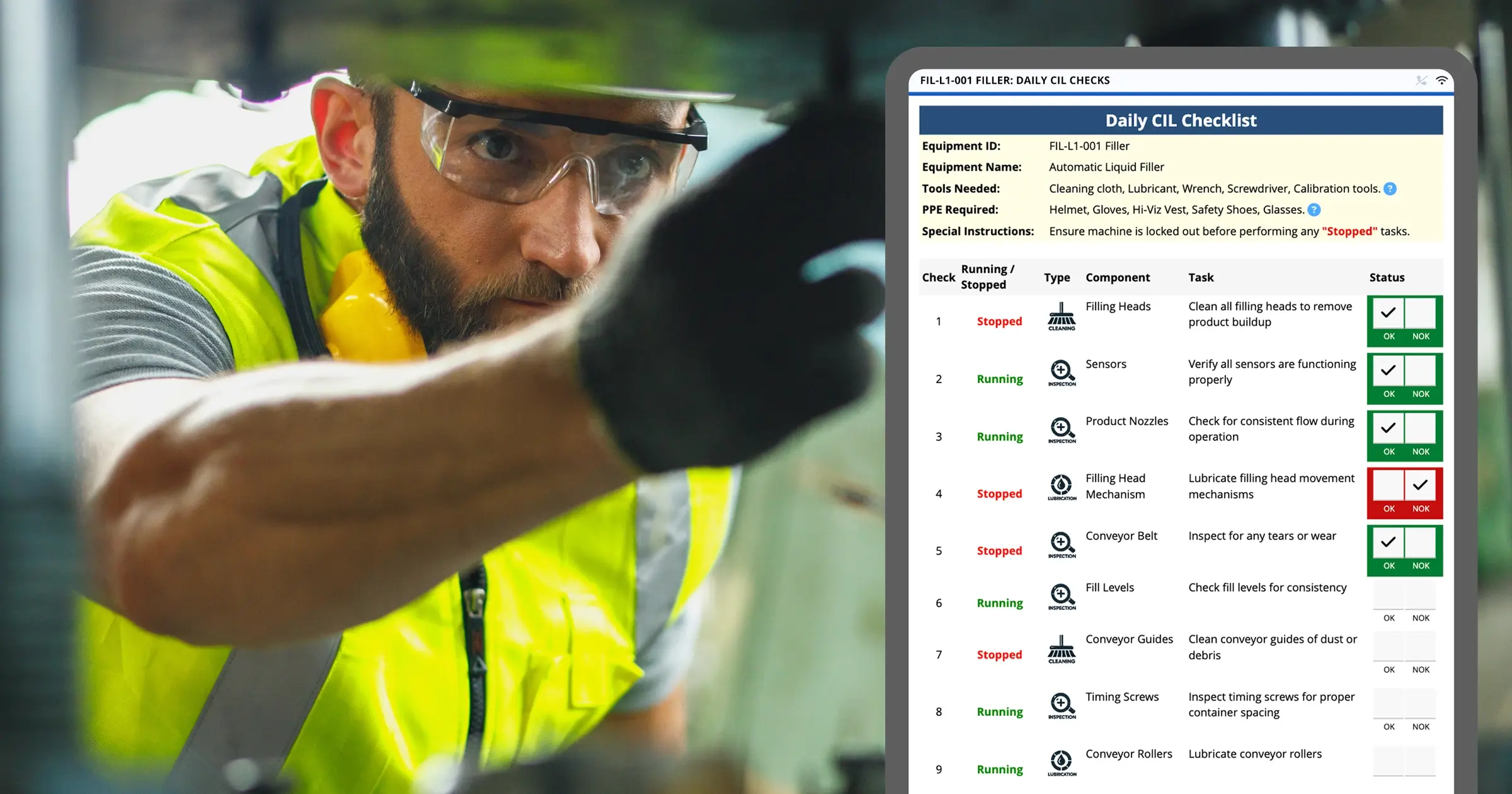
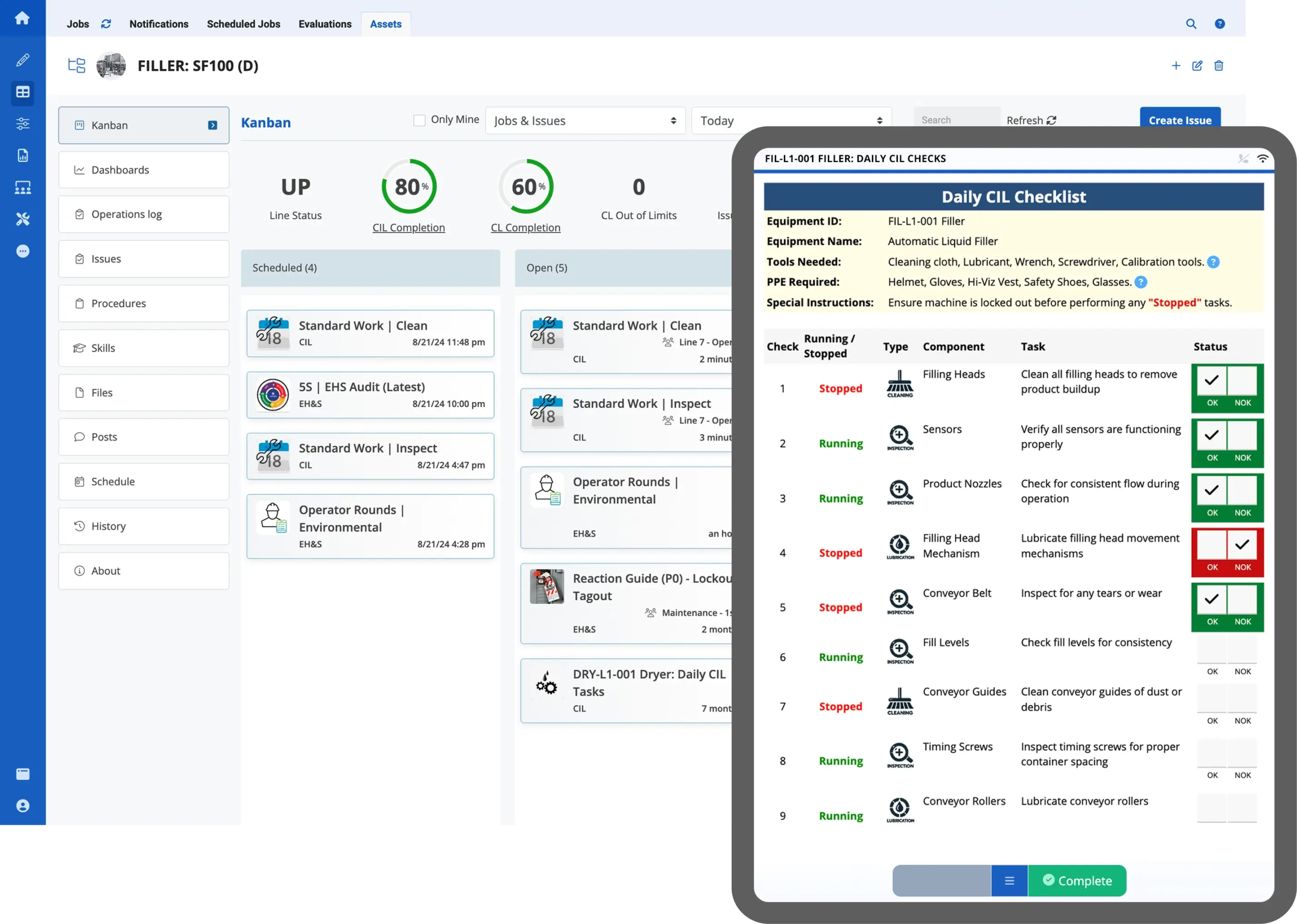
Encouraging operators to handle basic maintenance tasks—such as Clean, Inspect, Lubricate (CIL)—as part of an Autonomous Maintenance and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) strategy minimizes equipment downtime, improves machine efficiency, and ensures machines run at peak performance.
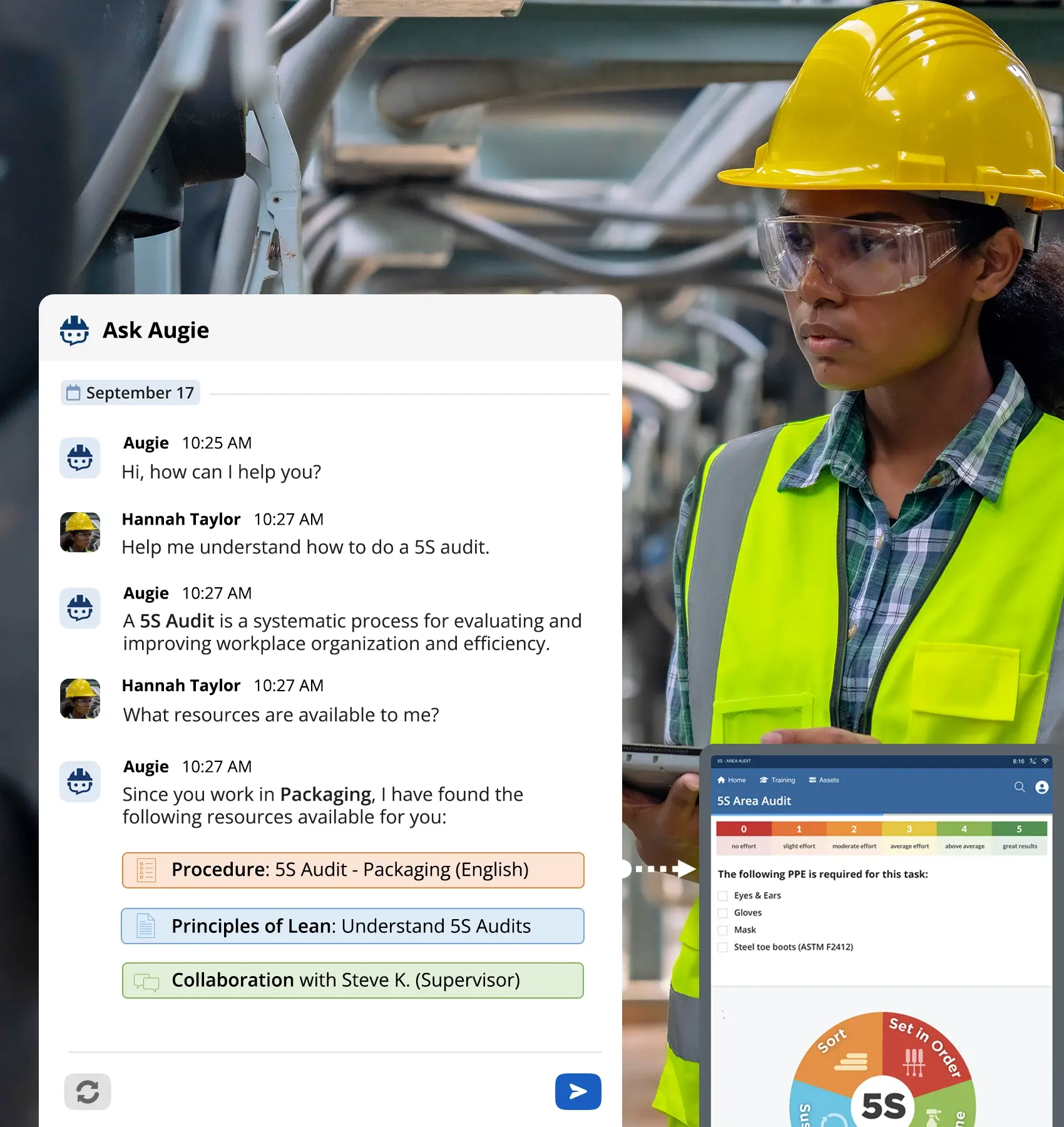
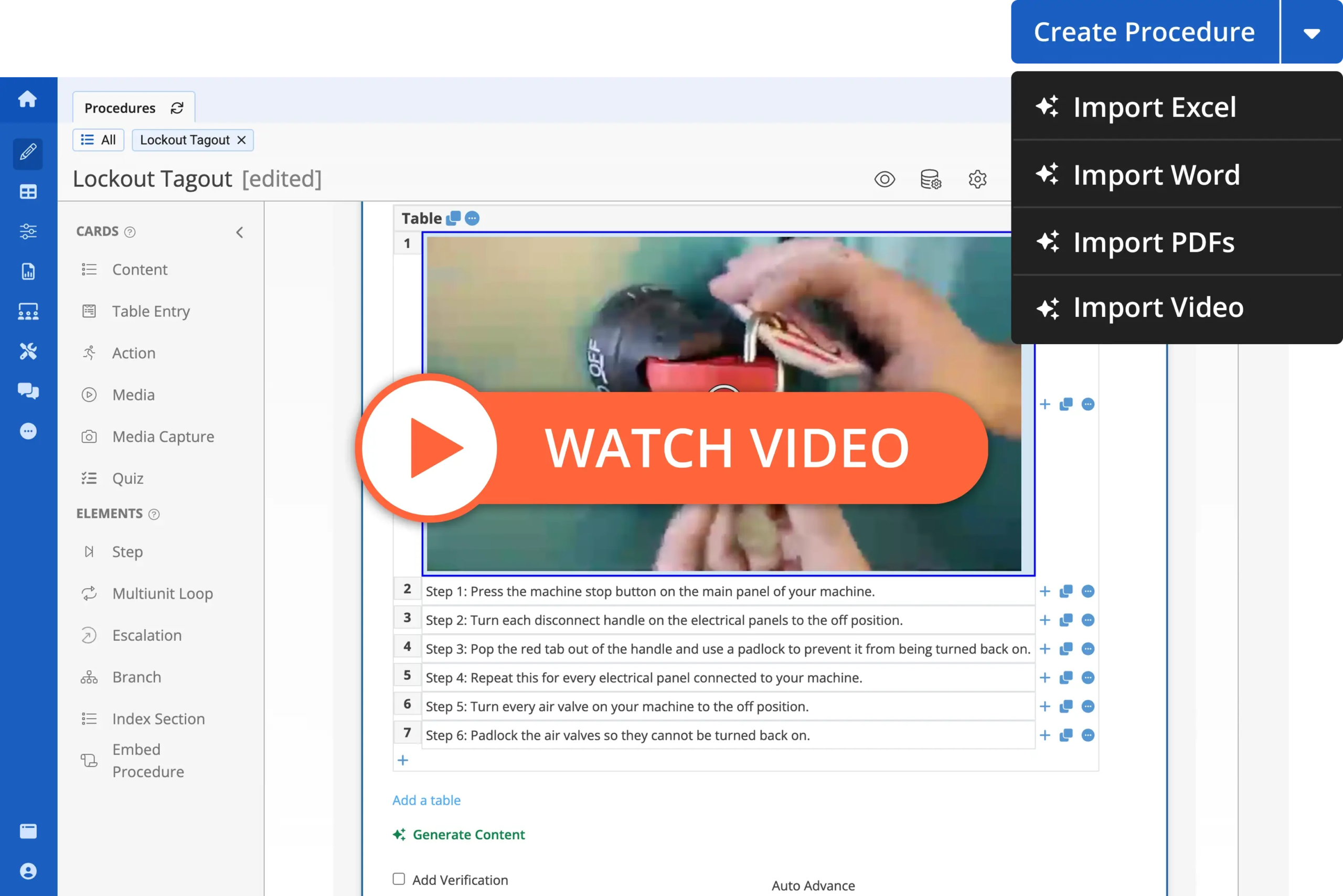
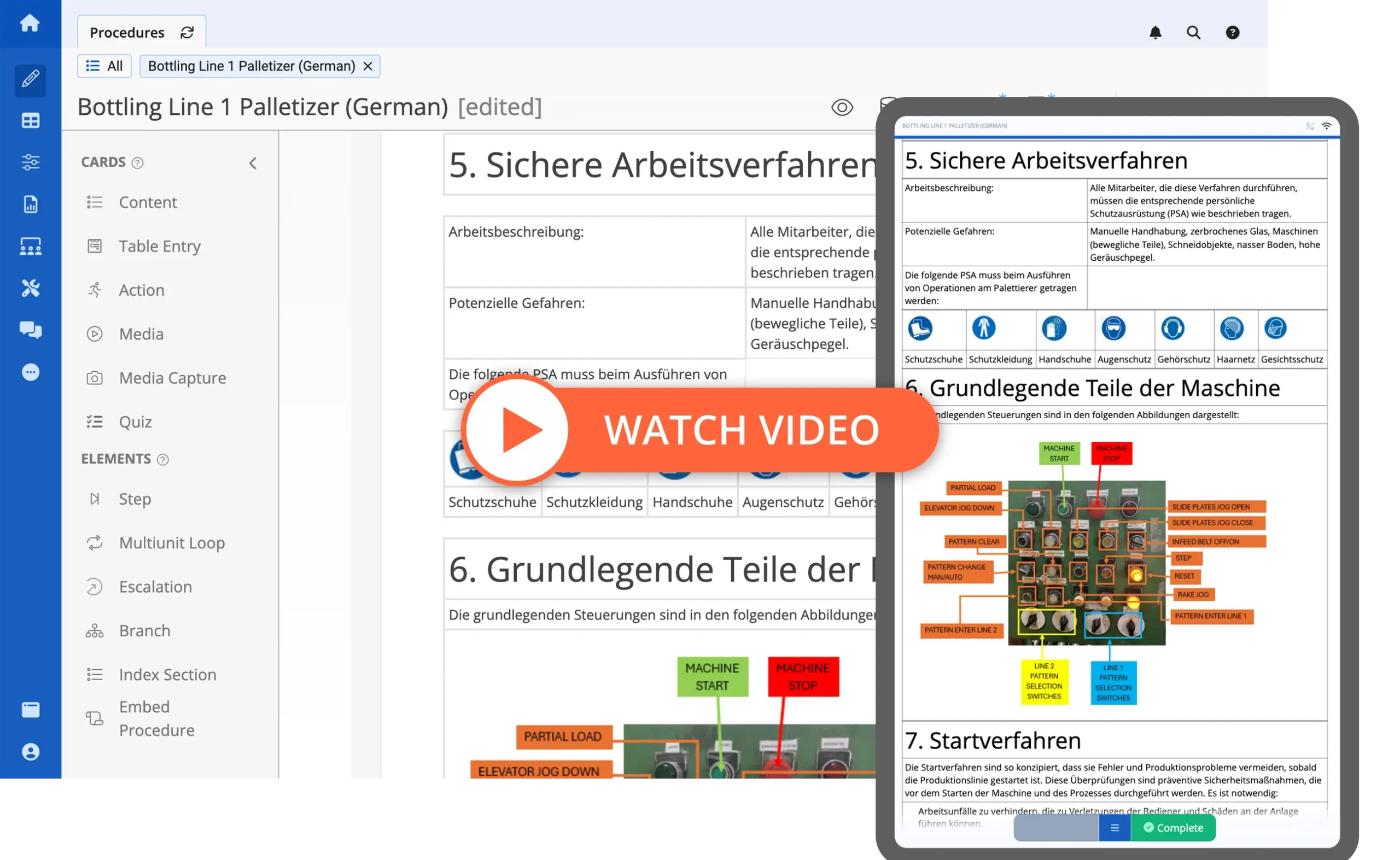
3. Leverage Digital Work Instructions and Connected Worker Tools
Modern digital approaches like digitizing standard operating procedures (SOPs) and adopting connected worker tools helps ensure consistency, reduce errors, and make it easier to train workers by providing accurate data.
In a recent survey conducted by LNS Research, more than 70% of the most profitable manufacturers are currently utilizing in Future of Industrial Work (FOIW) initiatives and connected worker technology, with the vast majority of them seeing meaningful progress and delivered corporate value through these workforce initiatives. Connected Worker platforms like Augmentir enable manufacturers to create AI-powered workflows that guide frontline workers through each task efficiently and accurately.
3. Use Real-Time Data and Analytics to Track Key Performance Indicators
Data-driven decision-making is critical for efficiency. Historical data can provide insights into the maximum output achieved by a facility under full capacity, which can help in defining standard outputs accurately. Real-time monitoring of machine performance, operator productivity, and process quality helps identify issues quickly and supports predictive maintenance strategies.
4. Streamline Workforce Management
Matching the right tasks to the right workers based on skills, experience, and availability reduces errors and idle time for any manufacturing company. Smart workforce tools can track training, performance, and certification to ensure optimal labor allocation.
Critical Components of Production Efficiency
Equipment Efficiency
Equipment efficiency is a critical component of production efficiency, as it directly impacts the overall productivity and effectiveness of the manufacturing process. Equipment efficiency refers to the ability of machinery and equipment to operate at optimal levels, with minimal downtime and maintenance. To achieve equipment efficiency, manufacturers can implement regular maintenance schedules, invest in modern and efficient equipment, and provide training to operators to ensure they are using the equipment correctly. By improving equipment efficiency, manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize downtime, and increase overall production efficiency. This not only enhances the reliability of the production process but also ensures that machinery operates at peak performance, contributing to higher output and better product quality.
Capacity Utilization
Capacity utilization is a key performance indicator (KPI) that measures the extent to which a manufacturing facility is using its available capacity to produce goods. It is calculated by dividing the actual output by the maximum potential output and is expressed as a percentage. Capacity utilization is essential for production efficiency, as it helps manufacturers identify areas of inefficiency and optimize their production processes. By improving capacity utilization, manufacturers can increase their production capacity, reduce costs, and improve product quality. High capacity utilization indicates that a manufacturing facility is effectively using its resources, leading to more efficient operations and better alignment with market demand.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a critical component of production efficiency, as it directly impacts the availability of raw materials and finished goods. Effective inventory management involves managing the flow of goods, services, and related information from raw materials to end customers. By implementing efficient inventory management systems, manufacturers can reduce waste, minimize stockouts, and improve overall production efficiency. Inventory management involves tracking inventory levels, managing supply chains, and optimizing inventory turnover to ensure that the right products are available at the right time. This not only helps in meeting customer demand promptly but also reduces the costs associated with excess inventory and stockouts, contributing to a more streamlined and efficient production process.
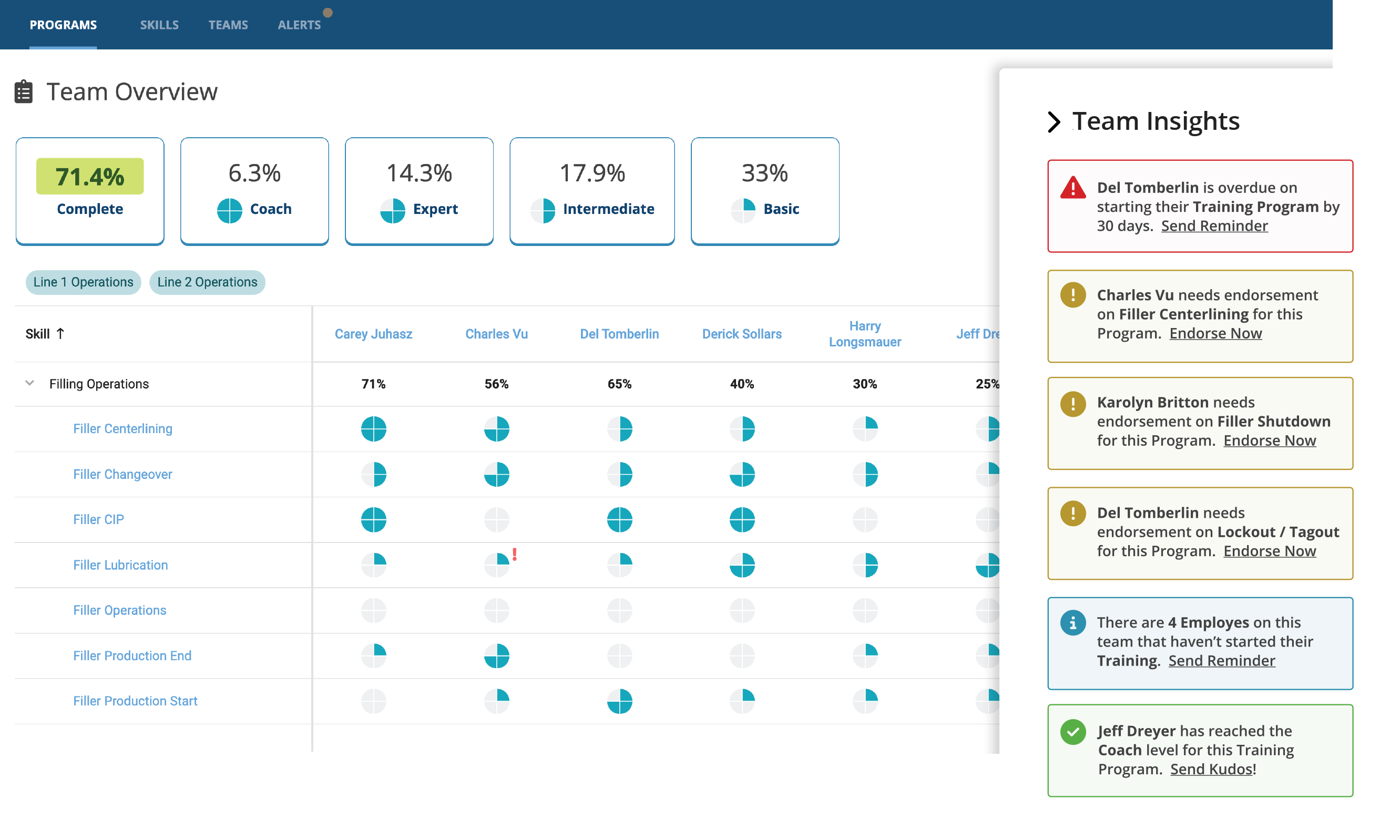
Workforce Management
Workforce management (WFM) is a critical component of production efficiency because it directly impacts how well human resources are aligned with operational goals. Here are the key reasons why:
- Optimal Staffing: WFM ensures the right number of workers with the right skills are available when needed, reducing overstaffing (which increases costs) and understaffing (which leads to delays or quality issues).
- Productivity Monitoring: Through tracking attendance, breaks, and output, WFM helps identify performance gaps and opportunities to improve workflow or training.
- Cost Control: Efficient labor scheduling and time management reduce overtime expenses, idle time, and unplanned labor costs.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Proper WFM systems help companies stay compliant with labor laws, union rules, and safety standards, reducing legal and financial risk.
- Employee Engagement: Transparent scheduling, fair workload distribution, and career development through performance data can boost morale and reduce turnover, which supports consistent productivity.
- Forecasting and Planning: WFM tools use historical data to predict future labor needs based on demand, helping operations run smoothly during peak and off-peak periods.
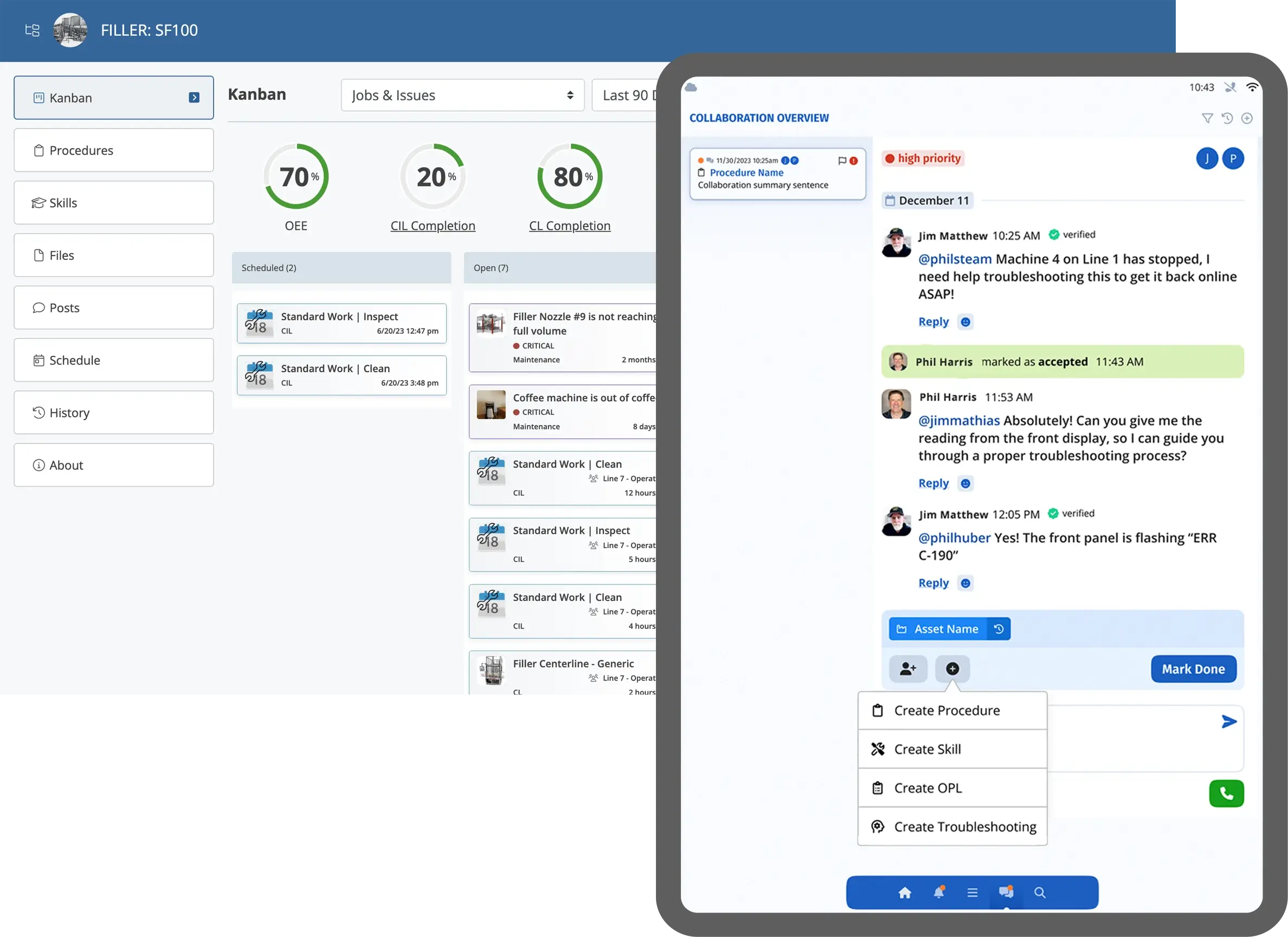
Connected worker platforms are a vital solution for workforce management because they digitize and streamline the way organizations engage with their frontline employees, enabling real-time communication, task coordination, and data capture. These platforms empower workers by providing instant access to schedules, training, and support tools, while giving managers visibility into performance and resource needs. By collecting operational data at the source, they support better forecasting, faster decision-making, and improved compliance with safety and regulatory standards. Ultimately, they enhance agility, reduce inefficiencies, and ensure that the workforce is aligned with evolving production demands.
Improving Production Efficiency with Augmentir
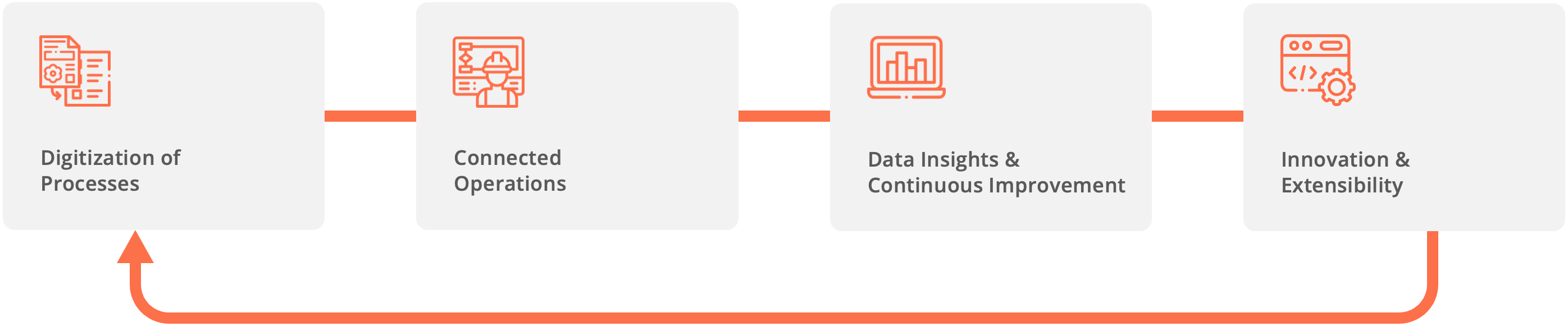
Modern manufacturing is increasingly driven by digital transformation. Tools like Industrial IoT (IIoT), AI-powered analytics, and connected worker platforms are revolutionizing how factories operate. These technologies provide visibility into operations, uncover hidden inefficiencies, and support agile decision-making.
Connected Worker Technology is transforming the way manufacturers approach production efficiency by bridging the gap between frontline workers and digital operations. These platforms equip workers with real-time access to information, interactive digital work instructions, and collaboration tools—right at the point of work. By digitizing tasks, capturing live performance data, and enabling guided workflows, connected worker solutions ensure that every job is done accurately, efficiently, and consistently.
With features like AI-driven insights, skills tracking, and remote expert support, Connected Worker platforms help manufacturers identify bottlenecks, reduce errors, and optimize workforce deployment. Tools such as Augmentir go a step further by personalizing guidance based on an individual’s skill level, automatically suggesting improvements, and helping identify opportunities for continuous training and upskilling. Ultimately, Connected Worker Technology empowers teams to work smarter, adapt faster, and drive sustainable gains in production efficiency.
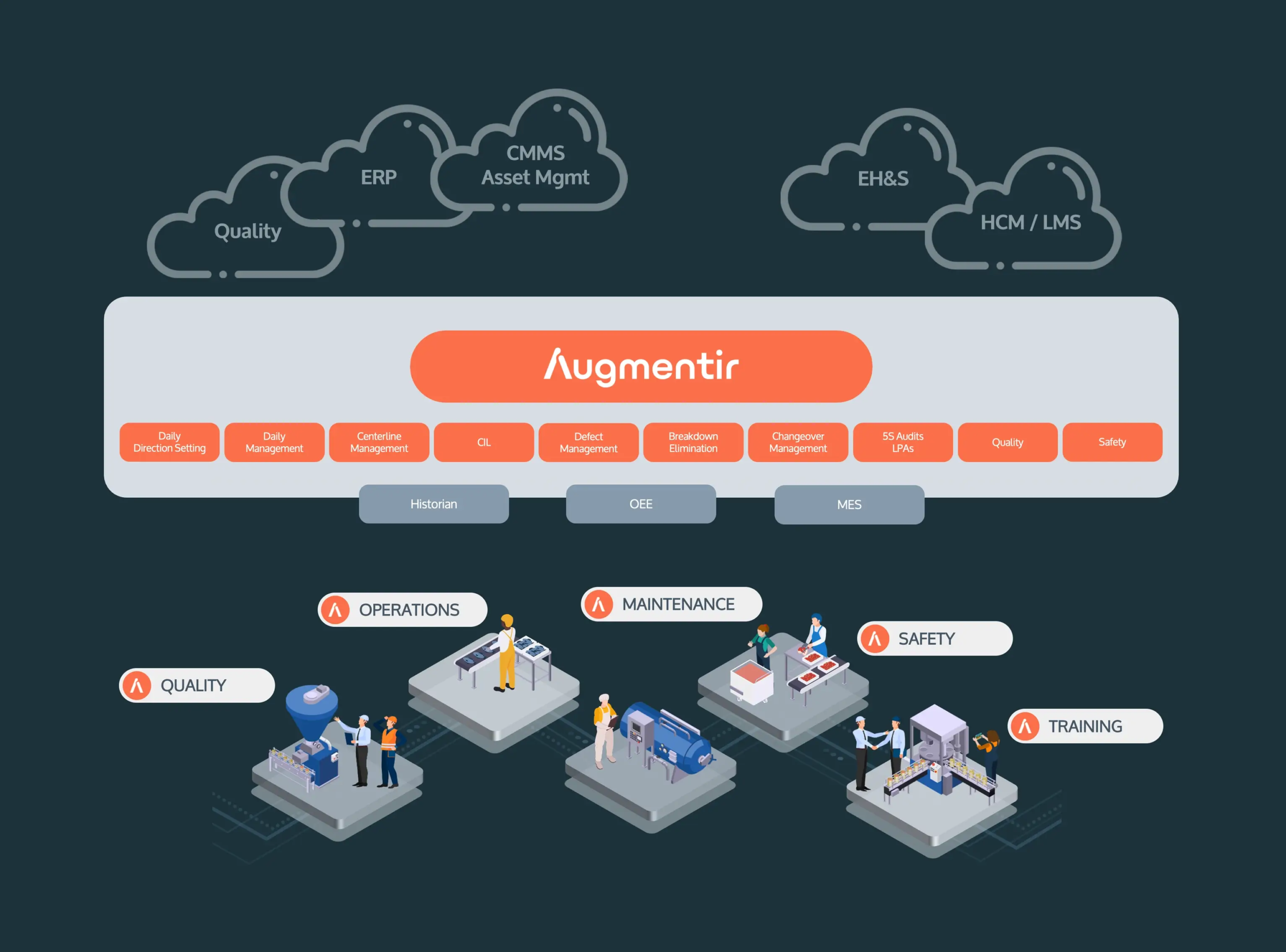
Augmentir serves as a digital frontline operating system for your lean strategy, and helps improve production efficiency. With Augmentir, you can digitize, manage, and optimize all aspects of your frontline operation:
- Daily Direction Setting (DDS)
- Daily Management System (DMS)
- Centerline Management
- Clean, Inspect, Lubricate processes
- Defect Management
- Breakdown Elimination
- Changeover Management
- Shift Handover
- 5S and Layered Process Audits
- Quality Management on the Shop Floor
- Safety
Contact us today for a live demo.


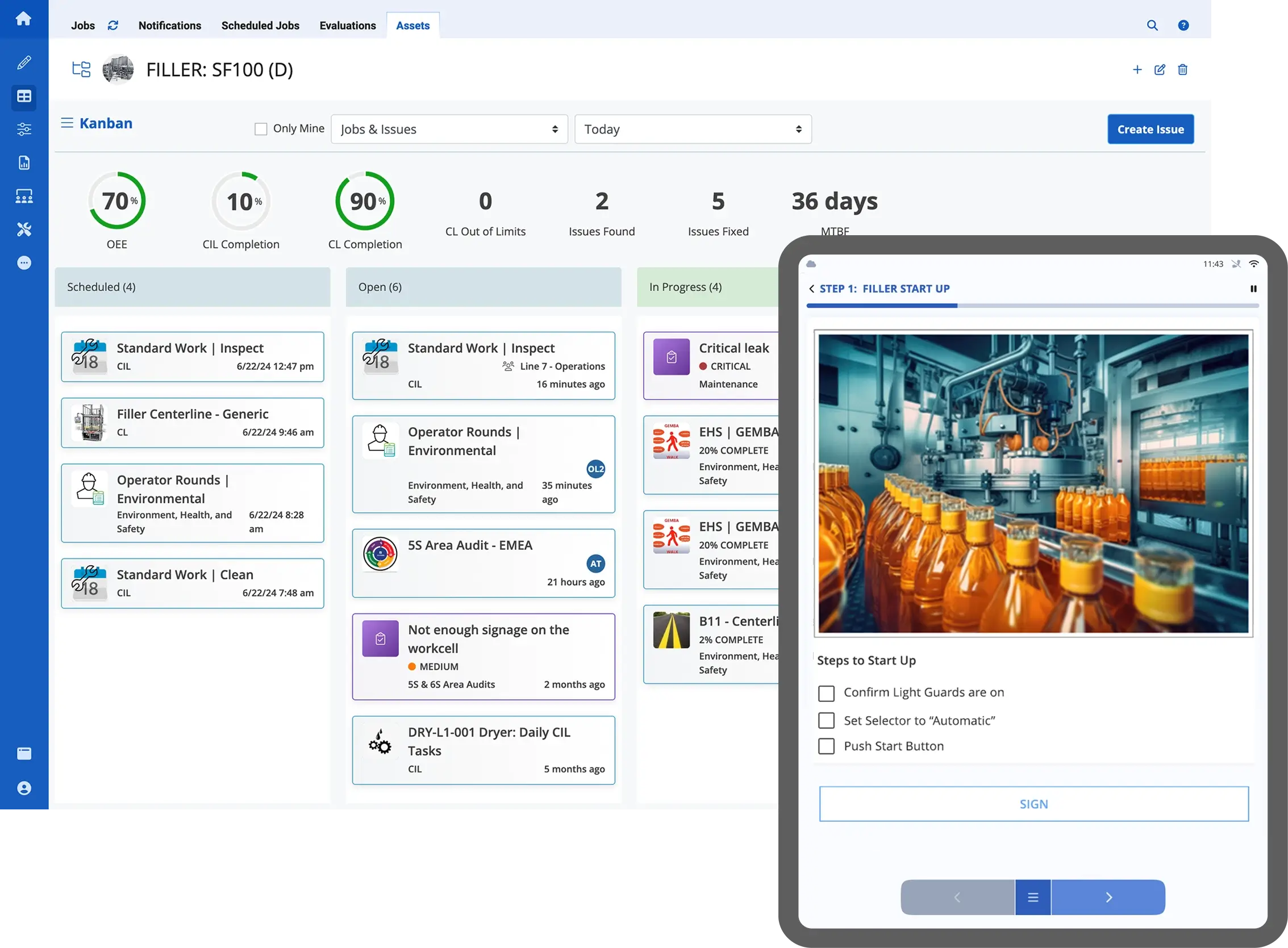
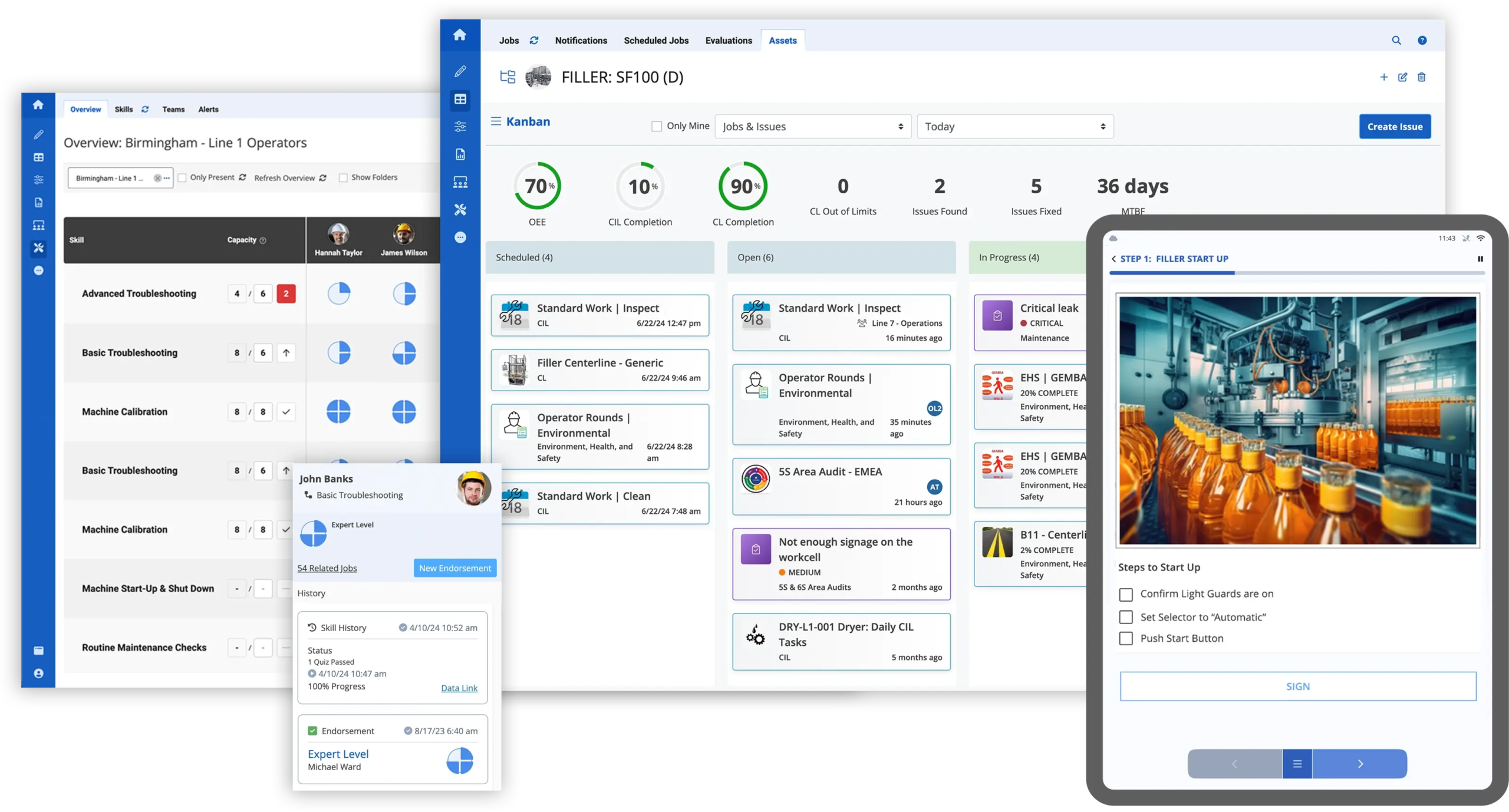
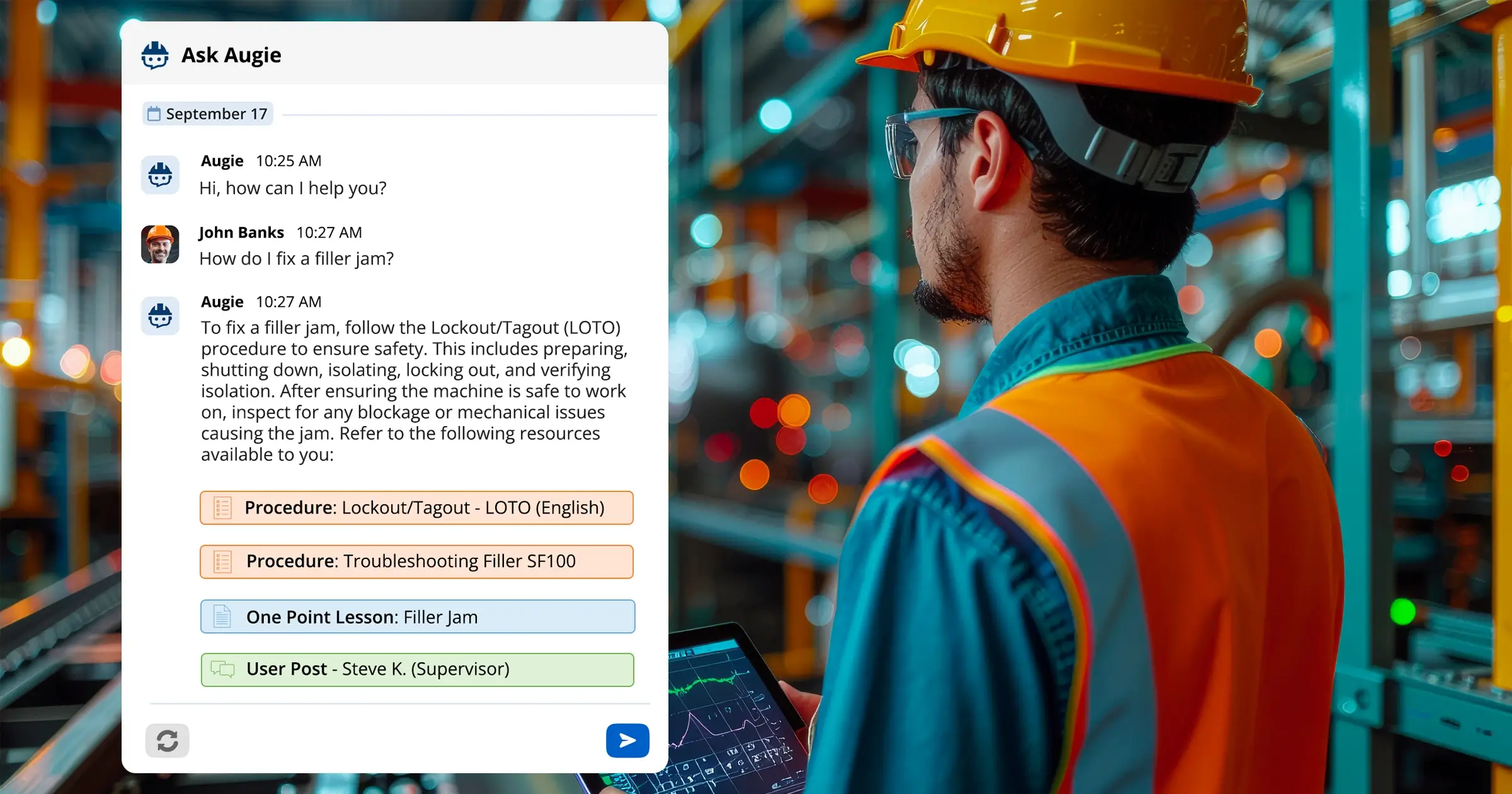

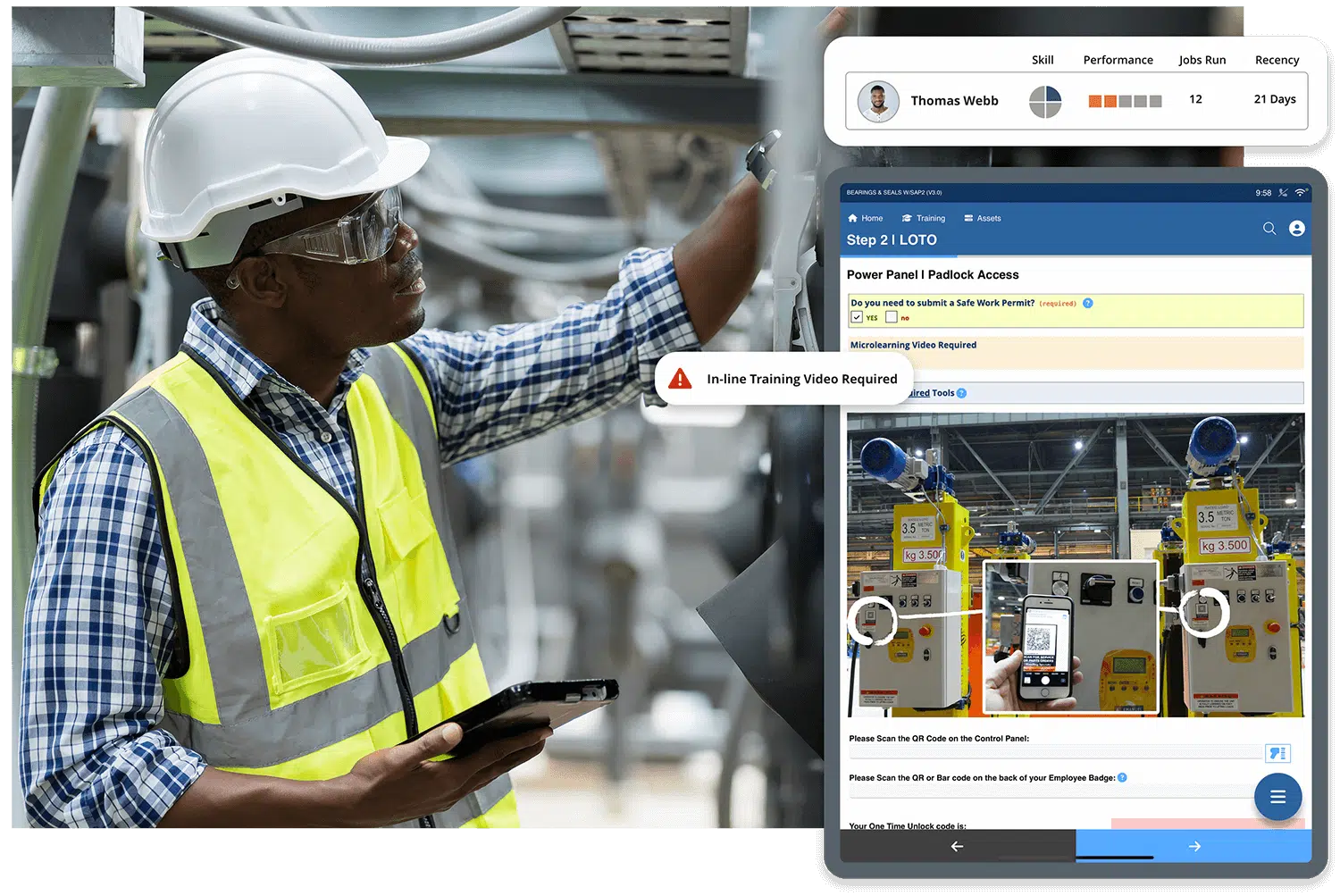 This kind of adaptive guidance is especially valuable in high-mix, low-volume environments or where production processes change frequently. Workers stay productive while learning in the flow of work—a win for both efficiency and engagement.
This kind of adaptive guidance is especially valuable in high-mix, low-volume environments or where production processes change frequently. Workers stay productive while learning in the flow of work—a win for both efficiency and engagement.