Learn the five steps to upskill and reskill manufacturing employees. Find out the benefits such as improving productivity and retention.
While the terms ‘upskill’ and ‘reskill’ in reference to manufacturing workers are often used interchangeably, they are not the same.
Upskilling refers to cultivating a worker’s skillset to help them excel in their current role. Meanwhile, reskilling involves teaching an employee new skills in order to transition to a new role.
For example, a programmer can be reskilled to become a systems analyst. Or workers can be upskilled to manage technology as more jobs become automated.
Half of all workers will need to be upskilled by 2025 as more jobs become digitized, according to the World Economic Forum. Workers will take on more critical thinking and problem-solving roles, leaving technical tasks to artificial intelligence and machine learning. Furthermore, the growing skilled labor gap in manufacturing has created a workforce shortage, and upskilling and training are becoming necessary to ensure production capacity is met.
Explore the following topics below to learn more about upskilling and reskilling in manufacturing, including a step by step guides to reskilling and upskilling manufacturing workers.
What does upskill mean?
Upskilling involves evaluating an employee’s existing skills and helping them to advance in their current role. It helps facilitate continuous learning by providing training opportunities to develop employee skills.
It can involve refining either soft skills or technical skills to fill workplace gaps. For instance, emotional intelligence is a soft skill that can be honed in leadership roles. Similarly, technical skills are needed in many manufacturing positions. Working with technology is a must as companies automate more and more of their operations.
An HR representative with data analytics experience, for example, can hone their skills to take on more specialized tasks. This can consist of taking a class to gain more knowledge or attending a virtual conference to learn about industry-specific technology.
Upskilling staff can help your business stay on top of industry trends and pivot in an ever-changing digital landscape.
What is reskilling?
Reskilling involves learning new skills to move on to a new role within a company. It’s also a cost-effective alternative to hiring new employees.
For example, an electrician may have excellent planning and job estimation skills. The organization could choose to reskill that worker to an estimation position instead of hiring someone from the outside.
Or an employer could reskill a production assembler to work as a maintenance technician. The new role may require taking a series of training courses and completing certain safety classes or certifications.
Reskilling and upskilling are efficient ways to retain a manufacturing workforce. Both provide opportunities to help workers grow and advance skills. Learn how to upskill and reskill staff with the following steps.
How to upskill manufacturing workers
It’s important to have a clear plan to upskill manufacturing workers:
Step 1: Assess current skills.
It’s crucial to map employees’ current skills. This data will serve as the baseline for measuring employee progress.
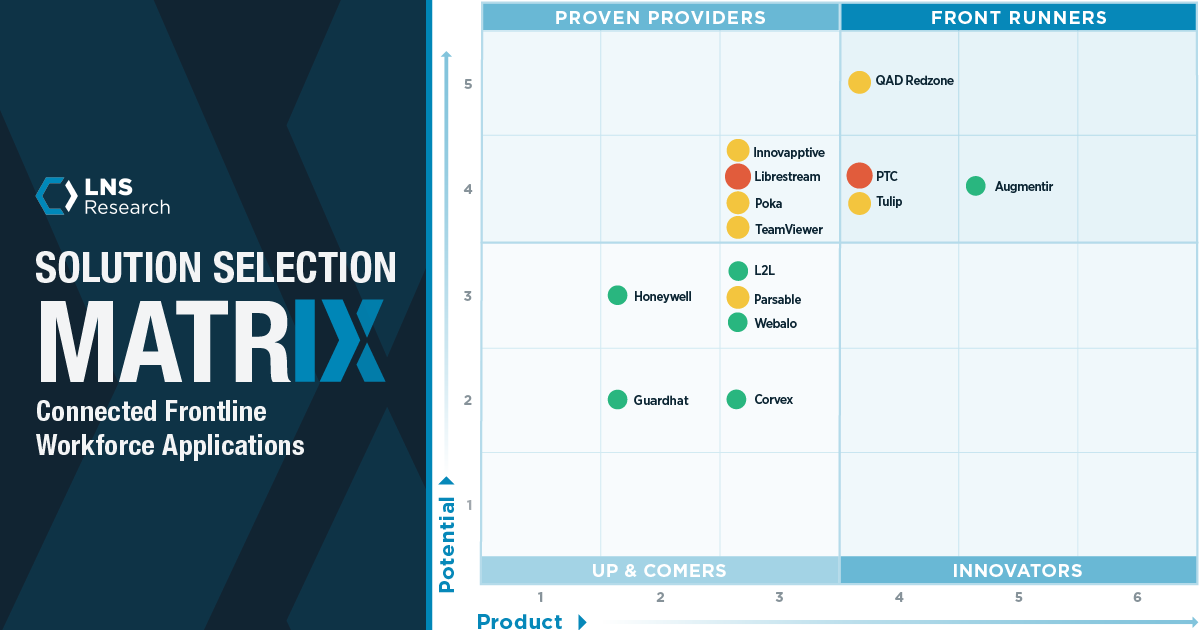
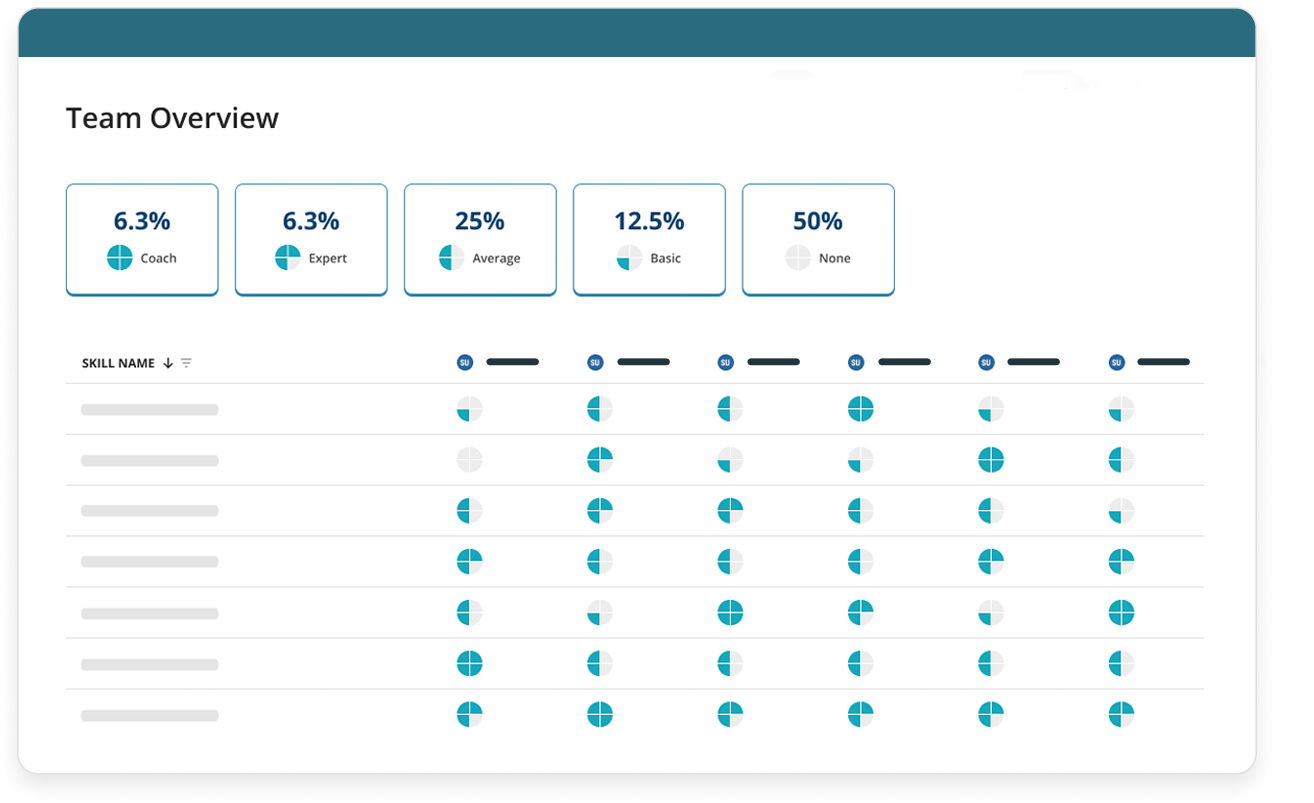
A great way to outline worker skills is through a skills matrix, which digitizes and helps accurately track skills across your organization. This can help identify any skills gaps that exist in current departments.
Step 2: Access skills needed for the future.
After assessing current employee skills, it’s time to identify any skills needed for the future. Keep in mind that these must align with any changes expected to occur in the manufacturing industry or in your long-term business plan.
Step 3: Create upskilling goals.
Set employee-specific goals. For example, you may want each worker to take training courses to hone job-specific skills.
Step 4: Match workers with new learning opportunities.
Workers can develop skills through new learning opportunities. It’s important to offer training and development opportunities that help workers grow and foster their skills.
Step 5: Monitor progress.
By this stage, you should have mapped employee skills and outlined which ones are needed. It’s important to monitor any progress made. Organizations that digitally track employee skills can map “what the worker has been trained on” to actual job performance (“how the worker is doing”) to create a true representation of proficiency gaps and upskilling opportunities.

How to reskill manufacturing workers
If you’re looking to reskill manufacturing workers, consider the following steps below:
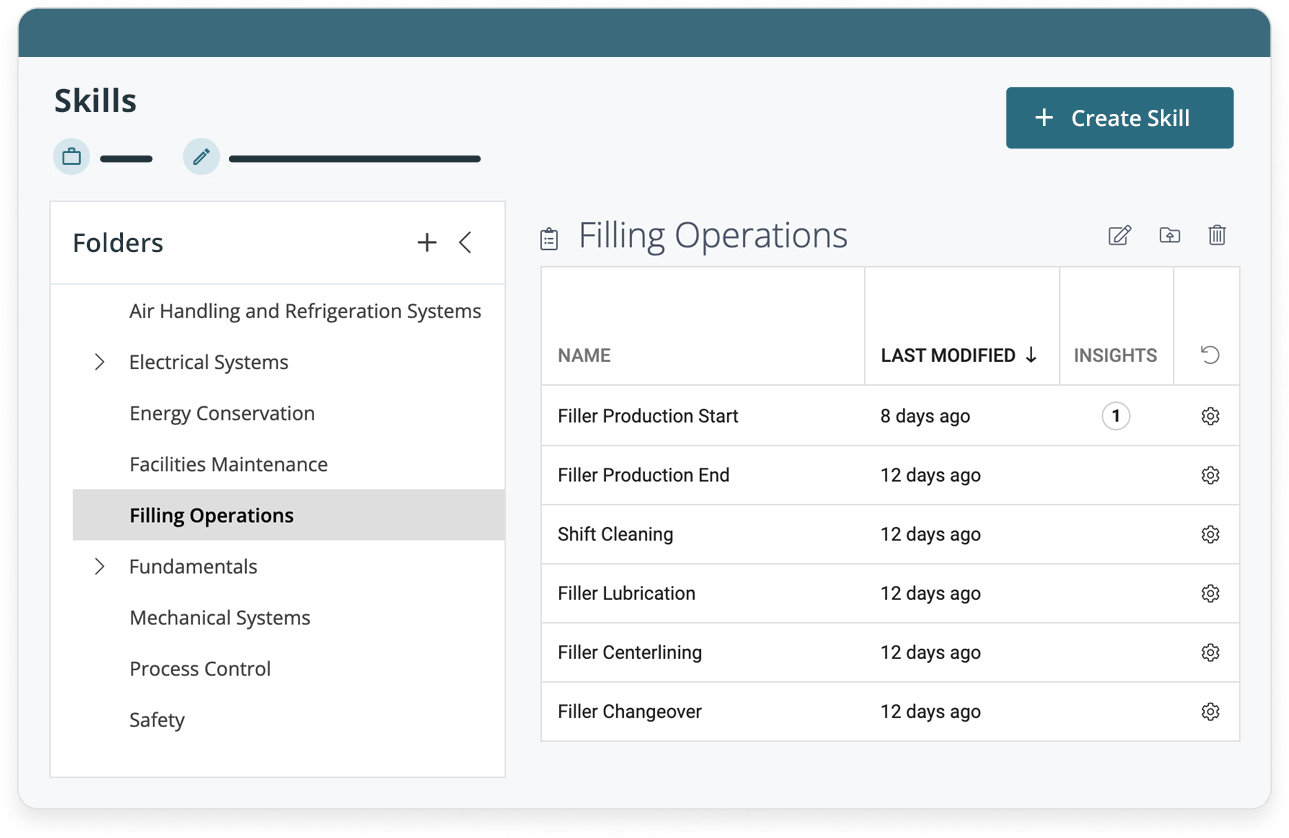
Step 1: Identify what skills need cultivating.
Pinpoint which skills are the most valuable and create training programs to train workers on those skills. Think about which new roles need to be created.
Step 2: Integrate upskilling.
It’s vital to start training employees and offering resources to advance skills. For example, training your workers on how to operate digital tools or a specific piece of equipment can help them take advantage of promotion opportunities down the line.
Step 3: Customize learning plan.
Develop a plan of core learning opportunities for any skillsets that are needed now or in the future. For example, you can customize learning plans to specific roles.
Step 4: Test and adjust.
Developing a perfect reskilling plan on the first try is no small feat. Be willing to acknowledge any mistakes and fix them.
Step 5: Invest in budget.
Allocating enough financial resources for reskilling employees is vital to company growth. Modify your budget to make reskilling a priority.
Benefits of upskilling and reskilling manufacturing employees
Workplace roles are changing and expanding in the age of automation. This change can bring about skill gaps that need to be filled for a business to stay ahead of the curve.
Upskilling and reskilling manufacturing employees has a number of long-term benefits for employers, such as:
- Boosts retention. Investing in your employees’ skills development fosters better relationships. Workers who feel valued are less likely to leave. Improving retention can save businesses money on hiring and training new workers.
- Improves morale. Businesses that offer training and development opportunities help their workers grow and move forward in the company. This can help employees feel like they’re working toward something and not staying stagnant within the company.
- Improves quality and productivity. Beyond retention and morale improvement, upskilling and reskilling can have production benefits. A more skilled and trained workforce can result in improved quality, productivity, and efficiency throughout your organization.
Looking to improve upskilling and reskilling within your organization?
Augmentir’s suite of smart connected worker tools helps manufacturing organizations create a more skilled and productive workforce. Find out how our software can make it easier to reskill and upskill manufacturing workers in your organization. If you’d like a demo, let us know and we’ll be in touch.